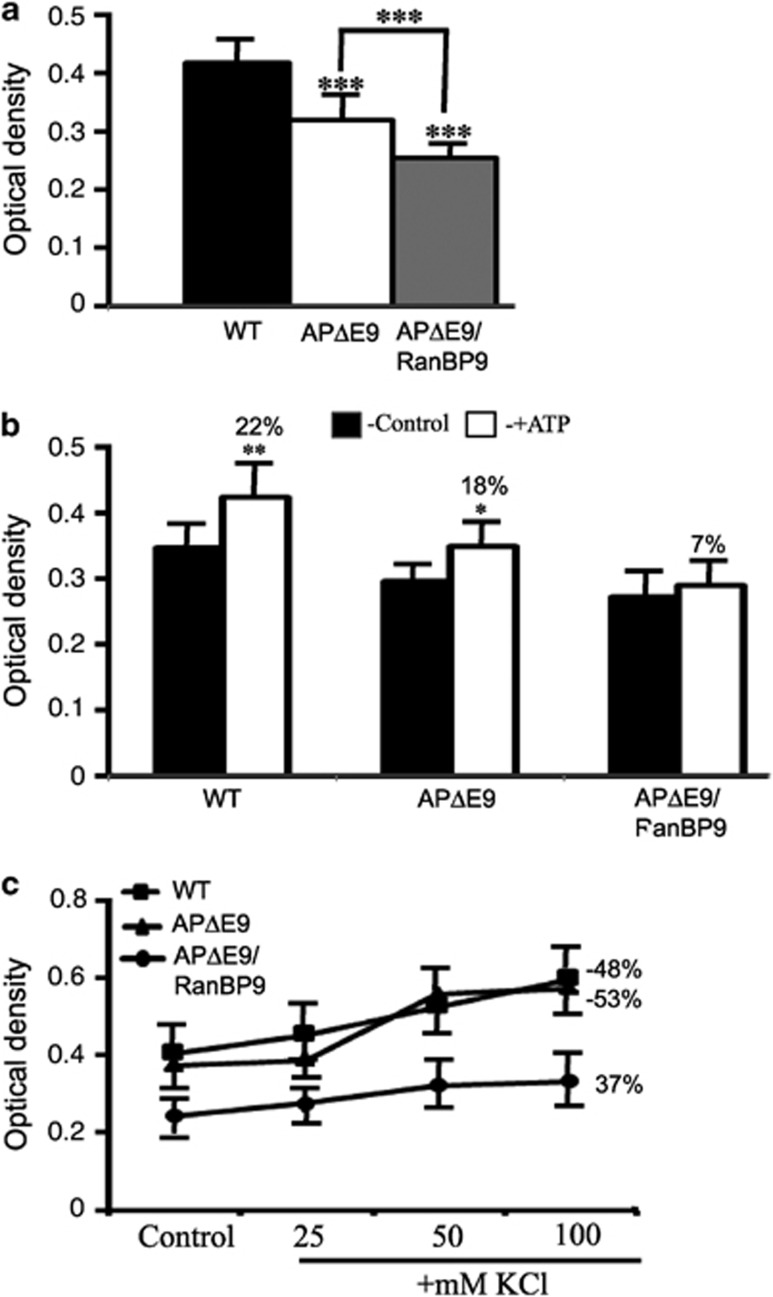
Figure 6.
RanBP9 exacerbates bioenergetic defects in the synaptosomes of APΔE9/RanBP9 mice. (a) Mitochondrial activity was measured as an index of synaptosomal functional integrity using MTT reduction assay. Basal mitochondrial activity in the synaptosomes was reduced by 23.3% in APΔE9 and by 39% in the APΔE9/RanBP9 mice compared with WT controls. Importantly, we noted 32% reduced activity in the APΔE9/RanBP9 mice compared to APΔE9 mice. (b), Under ATP-stimulated conditions used at 10.0 μM, MTT formazan production was increased by 22% in the WT, 18% in the APΔE9 and only 7% in the APΔE9/RanBP9 synaptosomes. (c) Under KCl- stimulated conditions, used at 25, 50 or 100 mM concentrations mitochondrial activity was increased more in the WT and APΔE9 synaptosomes compared with APΔE9/RanBP9 mice. At 100 mM KCl, the increase in the activity was 48% in the WT, 53% in the APΔE9 and only 37% in the APΔE9/RanBP9 synaptosomes. ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's test revealed significant differences. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 ***P<0.001 in APΔE9/RanBP9 mice compared with WT mice or APΔE9 mice. The data are mean±S.E.M., n=4 in each group