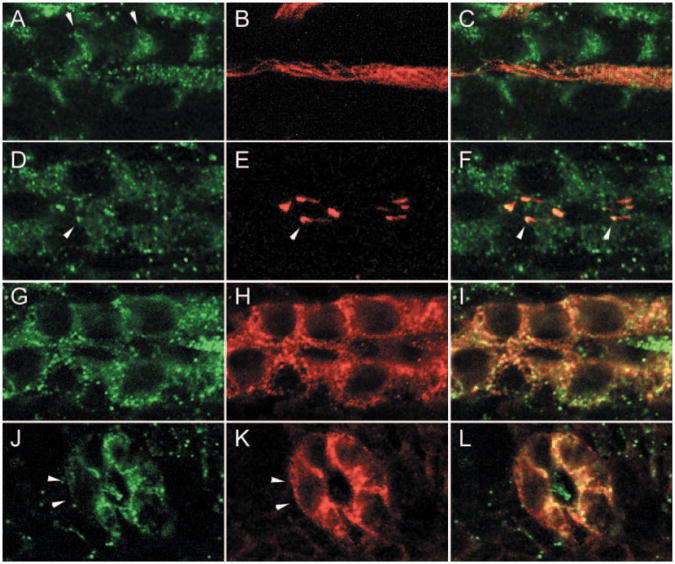
Figure 3.
Nephron segment-specific distribution of Polycystin-2 in basolateral membranes and cilia. (A through C) The anterior pronephric duct. Polycystin-2 (A; green) and acetylated tubulin (B; red) immunofluorescence in confocal sections. (C) Merged image of A and B. Anterior duct Polycystin-2 is present associated with basolateral membranes (arrows in A) and a lumenal bundle of cilia. (D through F) The posterior pronephric duct. Polycystin-2 (D; green) and acetylated tubulin (E; red) immunofluorescence in confocal sections. (F) Merge of D and E shows accumulation of Polycystin-2 in intracellular vesicles and at the base of cilia (arrows). (G through I) The anterior pronephric duct. (G) Tangential confocal section through the basolateral membranes shows a concentration of punctate Polycystin-2 expression in a whole mount-stained 2.5-d embryo. (H) Basolateral membranes of the anterior duct stain uniformly with the monoclonal α6F against the NaK ATPase α1 subunit. (I) Merge of G and H shows that Polycystin-2 and the NaK ATPase show areas of co-localization and some distinct areas of punctate expression. (J through L) The posterior pronephric duct. (J) Cross-section of the duct shows punctate Polycystin-2 immunofluorescence in lateral and apical membranes but absence of expression in basal cell surfaces. A lumenal cilium also is positive for Polycystin-2. (K) NaK ATPase immunofluorescence on basolateral membranes. (L) Merge of J and K.