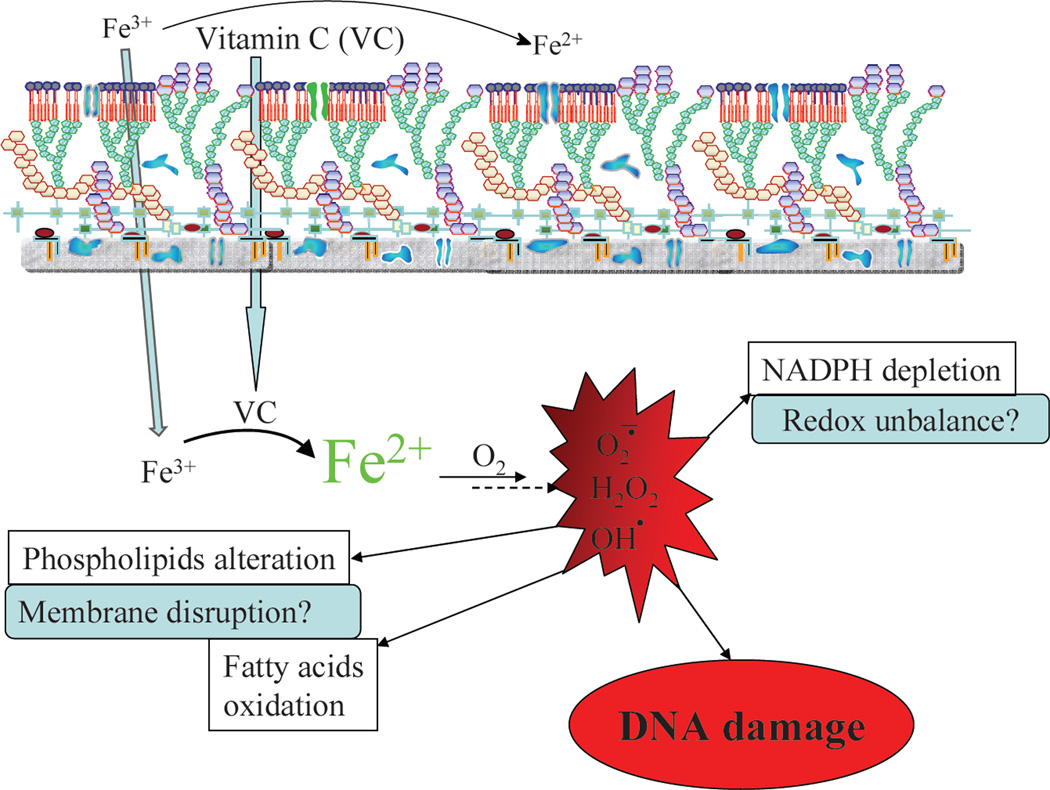
Figure 7. Schematic representation of the mechanism of action of vitamin C against M. tuberculosis.
Vitamin C enters M. tuberculosis cells and reduces ferric ions to generate ferrous ions which, in presence of oxygen, will produce superoxide, hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals via the Harber-Weiss and Fenton reactions. The production of these reactive oxygen species leads to the DNA damage, alteration of lipids and redox balance.