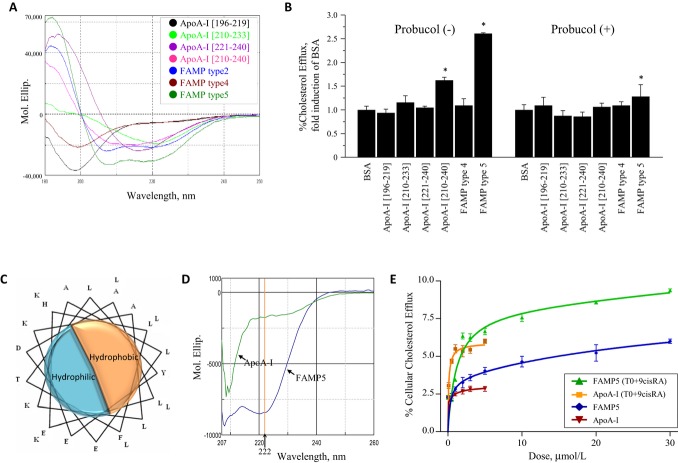
Figure 1.
Characteristics of human apoA‐I fragments and apoA‐I mimetic peptides. A, Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of human apoA‐I fragments and FAMP5 in water. The apoA‐I peptide fragment consisting of amino acids 210 to 240 was the only fragment in the region of apoA‐I that formed an α‐helical conformation. FAMP2 and FAMP5, but not FAMP4, formed strong α‐helical conformations. B, Effects of various human apoA‐I fragments and FAMPs on cellular cholesterol efflux in A172 human cells. Cellular cholesterol efflux mediated by apoA‐I fragments and FAMP4 and FAMP5 were measured in human A172 cells with or without probucol (10 μmol/L) in the presence of T0901317 (5 μmol/L) and 9‐cis‐retinoic acid (9cisRA; 5 μmol/L). The experiments were performed for 4 hours in the presence or absence of 20 μg/mL apoA‐I fragments, or FAMPs (n=3 to 5 for each group). C, Helix wheel representation of FAMP5. D, CD spectra of human apoA‐I and FAMP5 in buffer with 3 mol/L guanidine hydrochloride, 10 mmol/L Tris, and 5 mmol/L dithiothreitol (DTT). E, Dose‐dependent increases on a molar basis in human apoA‐I‐ and FAMP5‐mediated cellular cholesterol efflux for 4 hours are shown in the presence or absence of 5 μmol/L of T0901317 or 9‐cis‐retinoic acid in A172 cells (n=4 each). Values are mean±SD. *P<0.01 vs BSA group. FAMP indicates Fukuoka University apoA‐I mimetic peptide; apoA‐I, apolipoprotein A‐I; BSA, bovine serum albumin.