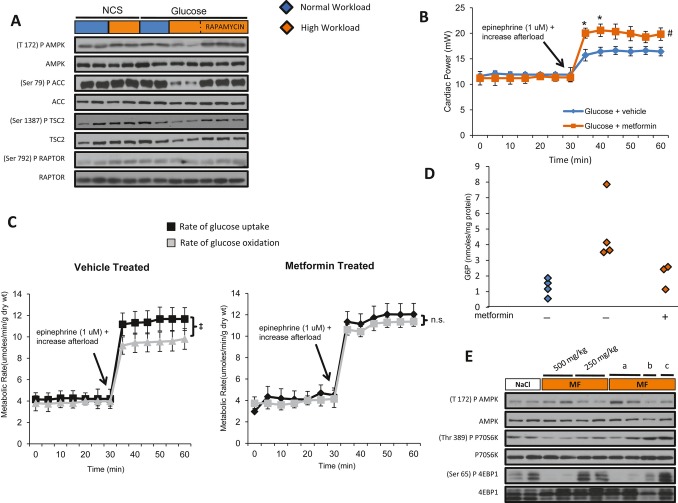
Figure 6.
G6P‐dependent mTOR activation is associated with downregulation of AMPK. A, Representative Western blots demonstrate reduction in phosphorylation of AMPK (T172) and ACC (S79), its downstream target, in hearts perfused with glucose at high workload. B, Contractile performance in the working heart perfused with glucose in the presence and absence of metformin. Data shown are mean±SEM; n=5 to 7 for each group. Metformin improves cardiac power at high workload. *P<0.05, #P=0.08, using Mann–Whitney rank sum test. C, Rates of glucose uptake and oxidation by hearts from animals receiving vehicle or metformin pretreatment for 7 days (vehicle treated, metformin treated). Data shown are mean±SEM; n=5 to 6 per group. Metformin treatment did not change rates of glucose uptake and oxidation at normal workload. At high workload, pretreating animals with metformin corrected the mismatch between rates of glucose uptake and oxidation. ‡P=0.021 using Mann–Whitney rank sum test. D, G6P levels in hearts from rats receiving either vehicle or metformin for 7 days before perfusion of their hearts with glucose as the only substrate. Dot plots of G6P show individual measurements for each heart at normal and high workloads. G6P accumulation was reduced in stressed hearts perfused with glucose in hearts of animals pretreated with metformin. Kruskal–Wallis test yielded an overall P=0.012. E, Representative Western blots demonstrating increased AMPK phosphorylation and decreased p70S6K as well as 4EBP1 phosphorylation in hearts from animals pretreated for 7 days with metformin (500 or 250 mg/kg) and perfused with glucose at high workload or in hearts from untreated animals perfused with glucose plus metformin at high workload. The concentrations of metformin in the perfusate were (a) 10 mmol/L, (b) 7.5 mmol/L, or (c) 5 mmol/L. Also see Table 1 for experimental detail. mTOR indicates mammalian target of rapamycin; AMPK, AMP kinase; ACC, acetyl‐CoA carboxylase; G6P, glucose 6‐phophate; MF, metformin.