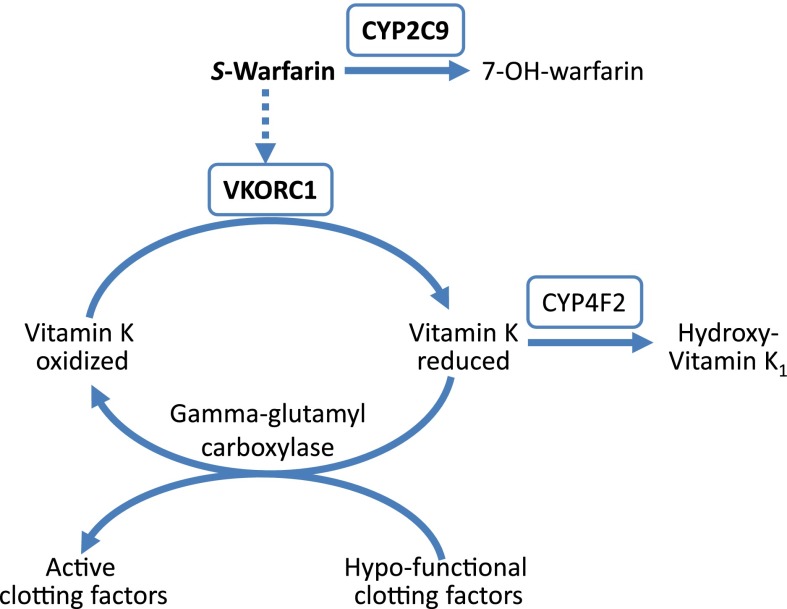
Fig. 2.
Warfarin pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic pathway. CYP2C9, cytochrome P450 2C9, metabolizes the more potent S-enantiomer of warfarin; VKORC1, vitamin K epoxide reductase complex 1, target site for warfarin; CYP4F2, cytochrome P450 4F2, metabolizes vitamin K. The genes for proteins shown in boxes are the primary genes influencing warfarin dose requirements.