Fig. 1.
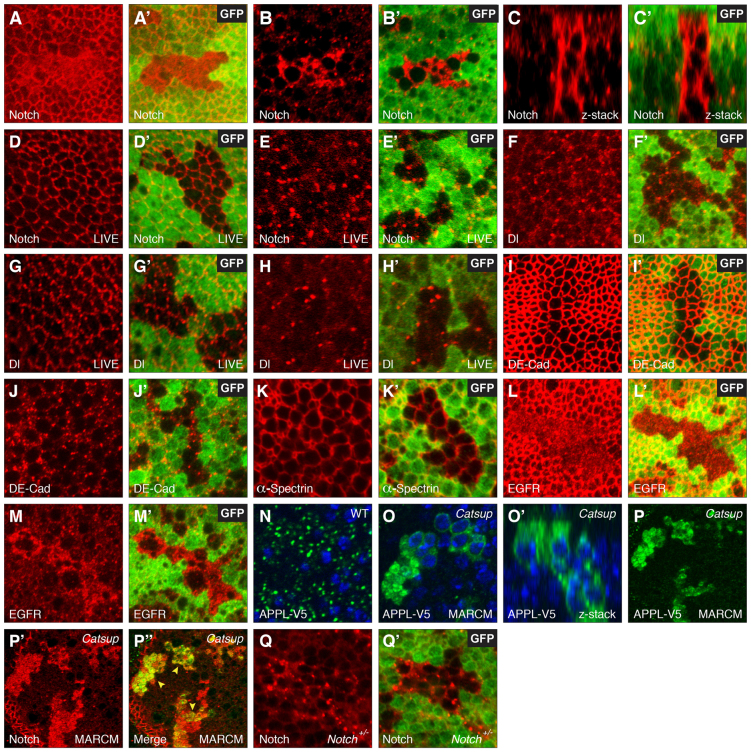
Notch accumulates abnormally in pre-endocytic compartments in Catsup mutant tissues. (A-M′) Confocal optical sections through Drosophila wing imaginal discs bearing homozygous mutant clones of Catsup, immunostained for specific proteins (red) together with the corresponding GFP signal (green) to identify clone locations in each image pair (absence of green signal in A′,B′,C′,D′,E′,F′,G′,H′,I′,J′,K′,L′,M′). (A-C′) Notch accumulation in apical membranes (A,A′) and basal cell regions (B,B′) of fixed tissue clones, and in a confocal z-series (C,C′) encompassing the apicobasal extent of the disc monolayer epithelium from apical (top) to basal (bottom). (D-E′) Distribution of newly endocytosed Notch in live tissue that was labeled with antibodies directed against the Notch extracellular domain prior to fixation, showing apical membranes (D,D′) and basal cell regions (E,E′). (F-H′) Delta (Dl) protein distribution in basal cell regions of fixed tissue (F,F′), apical membranes of live-stained tissue (G,G′) and basal cell regions (H,H′) of live-stained tissue. (I-J′) DE-Cadherin (DE-Cad; apical region in I,I′; basal region in J,J′). (K,K′) α-Spectrin distribution in fixed tissue clones. (L-M′) EGFR distribution in apical (L,L′) and basal (M,M′) regions of fixed tissue clones. (N) Distribution of epitope-tagged Amyloid Precursor-like Protein (APPL-V5) expressed under control of daughterless gene regulatory elements in wild-type control tissue. (O,O′) Accumulation of APPL-V5 (green) in Catsup mutant clones, shown in an apical view (O) and in an apicobasal confocal z-series (O′). Catsup clones were produced in wing discs using the MARCM system (Lee and Luo, 2001) to express APPL-V5 in clone cells only. Nuclei are counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (blue) in panels N-O′. (P-P′) Colocalization of transgenically expressed APPL-V5 (P; green signal) and endogenous Notch (P′; red signal) in fixed Catsup clone tissue; merged overlay of the confocal signals in P and P′ is shown in P′; yellow arrowheads indicate colocalized Notch and APPL-V5 overaccumulation. (Q,Q′) Notch accumulation in a basal cell region of a Catsup mutant clone in a N54l9/+ genetic background (Notch signal in red; GFP signal in green as in A-M′); heterozygous Notch larvae were identified by their reduced Cut expression at the DV boundary (see Materials and methods).