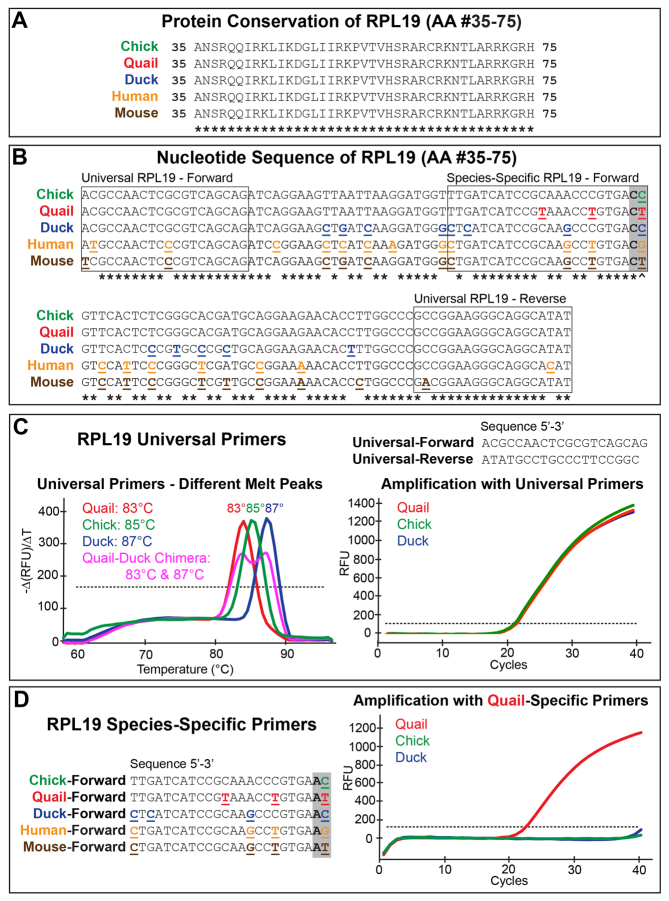
Fig. 2.
Analysis of RPL19 and generation of species-specific primers. (A) RPL19 sequence between amino acids 35 through 75. (B) Corresponding nucleotide sequence contains between 3 and 19 mutations per species (underlined and emboldened) compared to chick. Binding locations of universal and species-specific primers are shown. (C) Universal primers amplify evenly, yet due to nucleotide differences among species, melt peaks vary when plotted as the rate of change of relative fluorescent units (RFU) with time (T). Quail-duck chimeras show two melt peaks. (D) Five RPL19 species-specific primers with the distinguishing region and one added mismatch (C to A) at the 3′ end (gray box). The quail-specific primer only amplifies quail cDNA and not duck or chick.