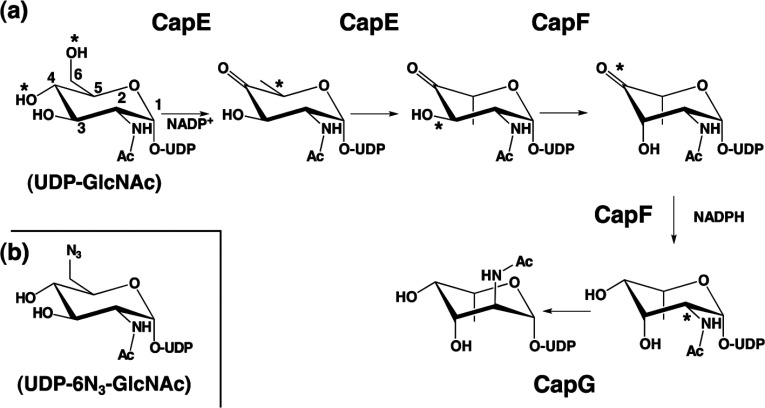
Figure 1. Biosynthetic pathway of UDP-L-FucNAc in S. aureus.
(a) Synthesis of UDP-L-FucNAc requires the sequential activity of enzymes CapE, CapF and CapG. The enzyme CapE is a bifunctional enzyme catalysing the 4,6-dehydration of UDP-D-GlcNAc and a subsequently C5-epimerization. CapF catalyses the C3-epimerization of the previous intermediate, followed by the reduction of the keto-sugar at position C4. CapG catalyses a C2-epimerization to yield the final product UDP-L-FucNAc. The asterisks indicate the chemical groups subjected to enzymatic modification. This pathway is adapted from previous mechanistic studies [12,14]. (b) Structure of the substrate analogue UDP-6N3-GlcNAc, where the hydroxyl group at C6 of the substrate is replaced by an azide substituent [20].