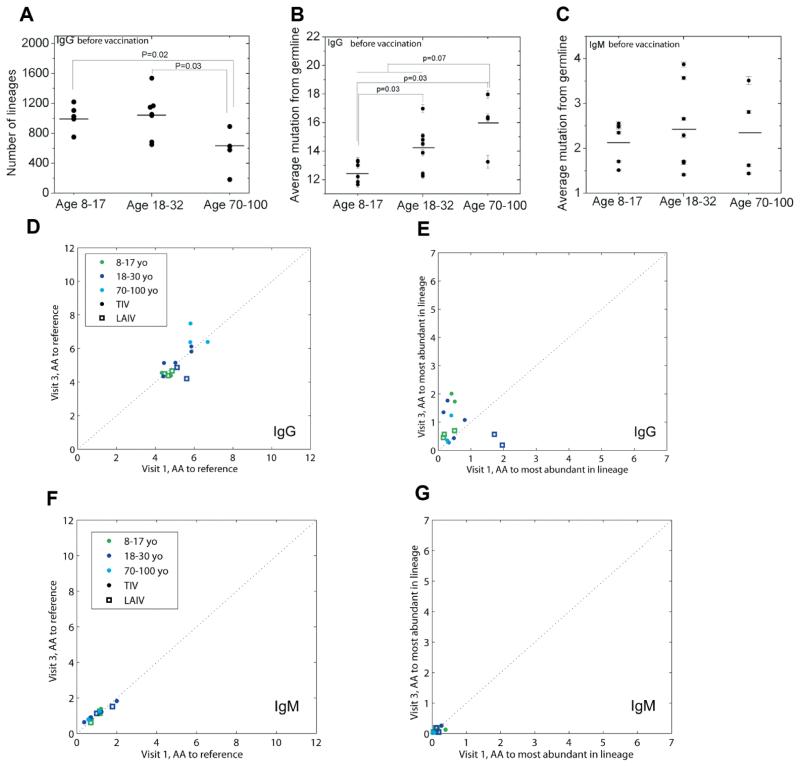
Fig. 3. Age related repertoire diversity and mutation changes.
(A), repertoire diversity changes with age as measured by number of lineages in IgG from visit 1 PBMCs. (B and C), before vaccination mutation load as measured by averaging mutations at nucleotide level for IgG (B) and IgM (C) in visit 1 PBMCs respectively. Mutations for each read were defined as the number of mismatches to germline reference in V, D and J regions. (D-G), lineage analysis, performed with 80% nucleotide-sequence identity at the VDJ junctional region, gives measurements of amino acid mutations-per-read at V and J gene segments measured either to the germline reference (D and F) or from the most abundant sequence of the lineage to which each belongs (E and G) for IgG (D and E) and IgM (F and G). X-axes denote the measurement at visit 1, and the Y-axes denote the measurement at visit 3. Elderly patients show a higher number of IgG mutations from the germline (comparing 8-30 year-olds to 70-100 year-olds gives p<0.075 before vaccination and p<0.0044 after; restricting this analysis to TIV-patients alone gives p<0.18 and p<0.017, respectively). 3000-read of subsampling was applied to all panels. All error bars are the standard error. p-values were calculated by Mann-Whitney U test.