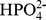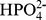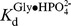Table 2. Summary of pH-independent Pi dissociation constants for AP active site nucleophile mutants.
| Residue 102 | Residue 166 |
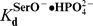 (M)a (M)a
|
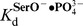 (M)b (M)b
|
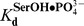 (M)c (M)c
|
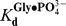 (M)d (M)d
|
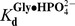 (M)e (M)e
|
| Ser | Arg | 4.6×10−7 | ≥1×10−7 | ≤2.9×10−13 | — | — |
| Gly | Arg | — | — | — | (∼1×10 −15 ) | (∼1×10 −8 ) |
| Ser | Ser | 1.1×10−4 | ≥2.5×10−6 | ≤6.9×10−11 | — | — |
| Gly | Ser | — | — | — | 2.1×10−13 | 9.3×10−8 |
—, not applicable.
Dissociation constant for 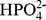 binding to deprotonated Ser102 as defined in Figure 4C from the measured pH-dependent Pi affinity in Figure 4A for R166S AP and Figure S9C for WT AP. Note that binding of
binding to deprotonated Ser102 as defined in Figure 4C from the measured pH-dependent Pi affinity in Figure 4A for R166S AP and Figure S9C for WT AP. Note that binding of 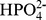 results in a proton transfer to the enzyme as illustrated in Equation 1;
results in a proton transfer to the enzyme as illustrated in Equation 1; 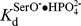 represents the observed overall binding.
represents the observed overall binding.
Lower limit of the dissociation constant for 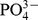 binding to deprotonated Ser102 AP determined as described in Text S6 and Figure S9.
binding to deprotonated Ser102 AP determined as described in Text S6 and Figure S9.
Upper limit for the dissociation constant for 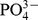 binding to protonated Ser102 AP as described in the main text and Figure 5.
binding to protonated Ser102 AP as described in the main text and Figure 5.
Dissociation constant for 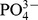 binding to S102G AP estimated from the measured
binding to S102G AP estimated from the measured 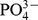 affinity of S102G/R166S AP and the expected contribution of Arg166 of 240-fold to the
affinity of S102G/R166S AP and the expected contribution of Arg166 of 240-fold to the 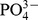 affinity (cf.,
affinity (cf., 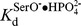 for WT and R166S AP). The dissociation constant for
for WT and R166S AP). The dissociation constant for 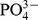 binding to S102G/R166S AP was determined from the pH-dependent binding data in Figure 4A and is defined in the model in Figure 4D.
binding to S102G/R166S AP was determined from the pH-dependent binding data in Figure 4A and is defined in the model in Figure 4D.