Figure 3.
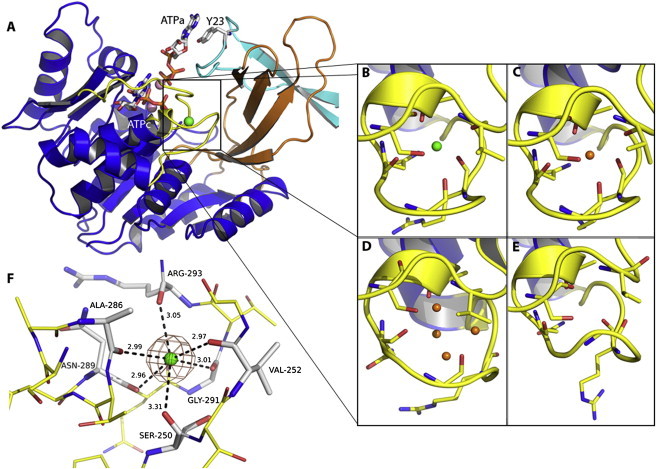
The monovalent cation-binding site of Pfk-2 from Escherichia coli. (A) Location of the cation binding site in the major domains (blue ribbons). The minor domain (orange ribbons) is shown packed against the partner subunit (cyan ribbons). The region around the Cs+ ion (green sphere) is formed by two loops (yellow), involving residues 288 to 296 and 244 to 254. Adjacent to this site the nucleotide substrate (ATPc) and the allosteric ATP (ATPa) sites are shown, highlighting the Y23 residue contributed from the partner subunit. The Mg2+ cations coordinated by the phosphoryl groups of ATPc and ATPa are represented as pink spheres. In panels (B to E), the side-chain residues around the cation-binding site are shown in licorice. (B) (PDBid 3UMP). The site is occupied by Cs+ (green sphere). (C) (PDBid 3N1C; chain A). In the presence of Na+ the site is organized around a single atom previously assigned as a water molecule (orange spheres). (D) (PDBid 3CQD, chain B). In the absence of cations the site is filled with four water molecules. (E) (PDBid 3N1C; chain D). The site could also be desolvated. (F) The coordination geometry of Cs+ (green sphere) and the carbonyl oxygen of the main chain are indicated by dashed lines.
