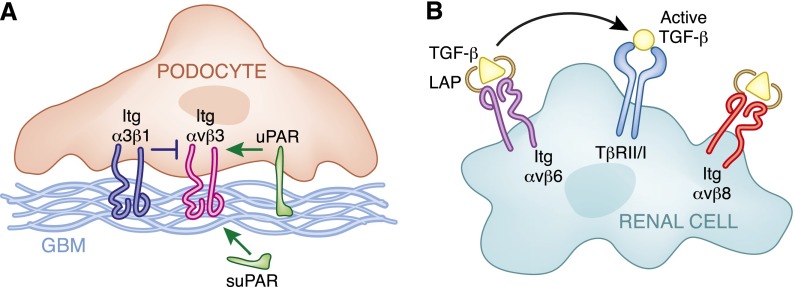
Figure 3.
αv integrins modulates glomerular ECM homeostasis by multiple mechanisms. (A) Schematic representations of mechanisms of activation (i.e., uPAR and suPAR) and inhibition (i.e., integrin α3β1) of integrin αvβ3 in podocytes that contribute to alterations in podocyte cell function. (B) In renal cells (i.e., tubular or mesangial cells), binding of the LAP/TGF-β complex to integrin αvβ6 contributes to release of active TGF-β and increased TGF-β receptor–mediated signaling. In contrast, binding of the LAP/TGF-β complex to integrin αvβ8 sequesters TGF-β, thereby decreasing TGF-β–mediated signaling.