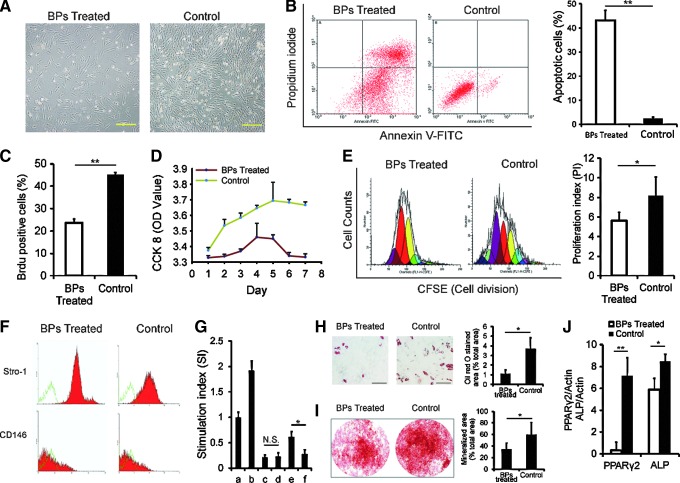
FIG. 2.
Impairment of biological and immunological functions of BMMSCs in the BP-treated minipigs. (A) BMMSCs in the BP group could hardly adhere compared with controls 1 week after isolation (scale bar=2.0 mm). (B) Annexin V staining for apoptosis showed that ∼43% of BMMSCs from the BRONJ group were positive for the early or late stages of apoptosis, but fewer apoptotic cells (4.14%±0.6%) were found in the untreated control group (**P<0.01). (C) Quantified BrdU-positive cells were significantly decreased in the BP-treated groups (**P<0.01). (D) CCK-8 tests showed a decreased proliferative ability of cells in the BP groups compared with the untreated group. (E) The carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) test indicated a declined proliferation index (*P<0.05) in the treatment group compared with the untreated control group. (F) There was no significant difference between the treatment and untreated control groups for both the Stro-1 and CD-146 markers (Stro-1: 64.38%±1.19% vs. 64.46%±0.93%; CD-146: 58.89%±0.42% vs. 55.17%±0.81%, both P>0.05). (G) In mixed lymphocyte reaction, when tested with CCK-8, there was no difference in the stimulation index between the BP and control groups (0.19%±3.2% vs. 0.21%±4.3%, P>0.05), when mixed PBLs and BMMSCs, in the presence of phytohemagglutinin (PHA), the stimulation index increased in the BP groups (0.57%±9.6% vs. 0.22%±6.5%, *P<0.05) (a: PBLs; b: PBLs+PHA; c: PBLs+BMMSCs of BP groups; d: PBLs+BMMSCs of control group; e: PBLs+PHA+BMMSCs of BP groups; f: PBLs+PHA+BMMSCs of control group). (H) The differentiation potential of BMMSCs stained with Oil red O or (I) alizarin red S (scale bar=50 μm) is shown; BMMSCs from BP-treated animals have significantly lower adipogenic differentiation and osteogenic differentiation potential (**P<0.01). (J) Q-PCR showed that PPARγ2 and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were expressed. Adipose potential, as well as osteogenic potential, was significantly different between the treatment and untreated control groups (**P<0.01; *P<0.05).