Fig 4.
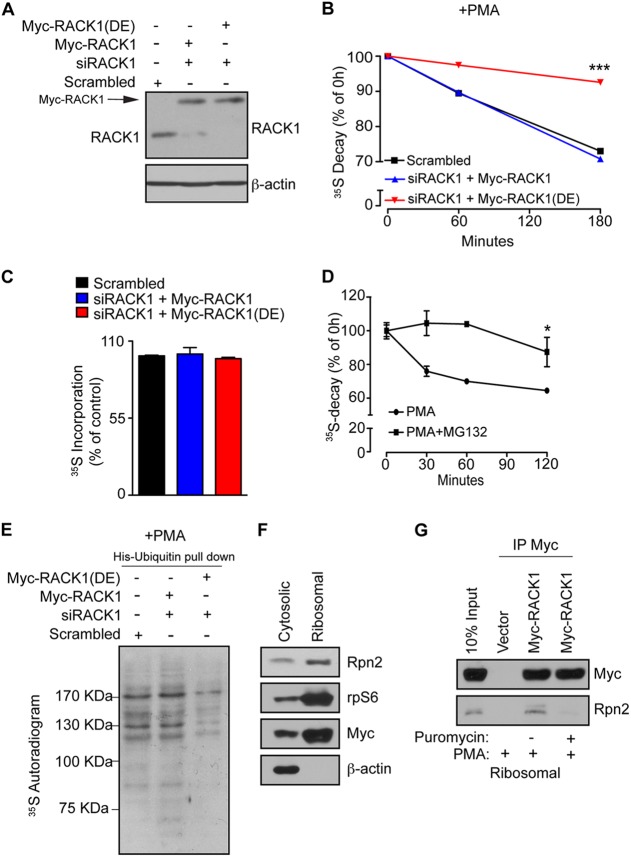
Association of RACK1 with ribosomes is required for ubiquitination and degradation of NSPs. (A) HEK293T cells were transfected with RNAi-insensitive Myc-RACK1 or Myc-RACK1R38D/K40E [Myc-RACK1(DE)], upon which the endogenous RACK1 was depleted using RACK1-specific siRNA (siRACK1). Scrambled siRNA was used as a control. The expression of the indicated constructs and the efficiency of RACK1 depletion were monitored by Western blotting. A total of 30 μg of the indicated cell lysate were loaded onto SDS-PAGE gels. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) The cells described in panel A were treated with 50 nM PMA for 30 min, and the stability of the NSPs was monitored by 35S pulse-chase (see Materials and Methods) after 1 and 3 h. Values obtained upon transfer of cells to cold media (0-h time point) were set to 100%, and data are represented as a mean values ± the SEM (n = 3). The expression of Myc-RACK1R38D/K40E significantly increased the stability of 35S-labeled polypeptides (P = 0.0006 compared to control cells at the 180-min time point; ANOVA, F3,8 = 62.62, P < 0.0001). (C) In contrast to the degradation of NSPs, protein synthesis was largely unaffected, as demonstrated by the lack of differences in the 35S incorporation after 30 min of labeling with [35S]Met-Cys. The data are represented as mean values ± the SEM (n = 3). (D) HEK293T cells were treated with PMA (50 nM) or PMA in combination with the proteasome inhibitor (50 nM PMA plus 50 μM MG132) for 2 h, and NSP degradation was monitored at 30-min, 60-min, and 2-h time points. Inhibition of the proteasome significantly attenuated the degradation of NSPs compared to untreated cells (Student t test, P = 0.0008 after 120 min). Values are represented as means ± the SEM (n = 3). (E) Cells described in panel A were transfected with His-ubiquitin, treated as in panel B, pulse-labeled with [35S]Met-Cys for 30 min, and subjected to His-ubiquitin pulldown under denaturing conditions (see Materials and Methods). The levels of ubiquitinated 35S-labeled NSPs were monitored by 35S autoradiography. (F) Cells expressing Myc-RACK1 WT (Myc-RACK1) were treated with 50 nM PMA for 30 min and fractionated into cytosolic and polysomal fractions. Portions (30 μg) of protein extracts from each fraction were used to monitor the distribution of the indicated proteins by Western blotting. rpS6 and β-actin served as markers for polysomal and cytoplasmic fraction, respectively. (G) Cells expressing Myc-RACK1 WT (Myc-RACK1) and control cells transfected with an empty vector were treated with a vehicle (0.1% DMSO), 50 nM PMA, or 50 nM PMA in combination with 100 μg of puromycin/ml for 30 min, fractionated as in panel F, and polysomal fractions were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Myc antibody. Immunoprecipitates and input (10%) were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies.