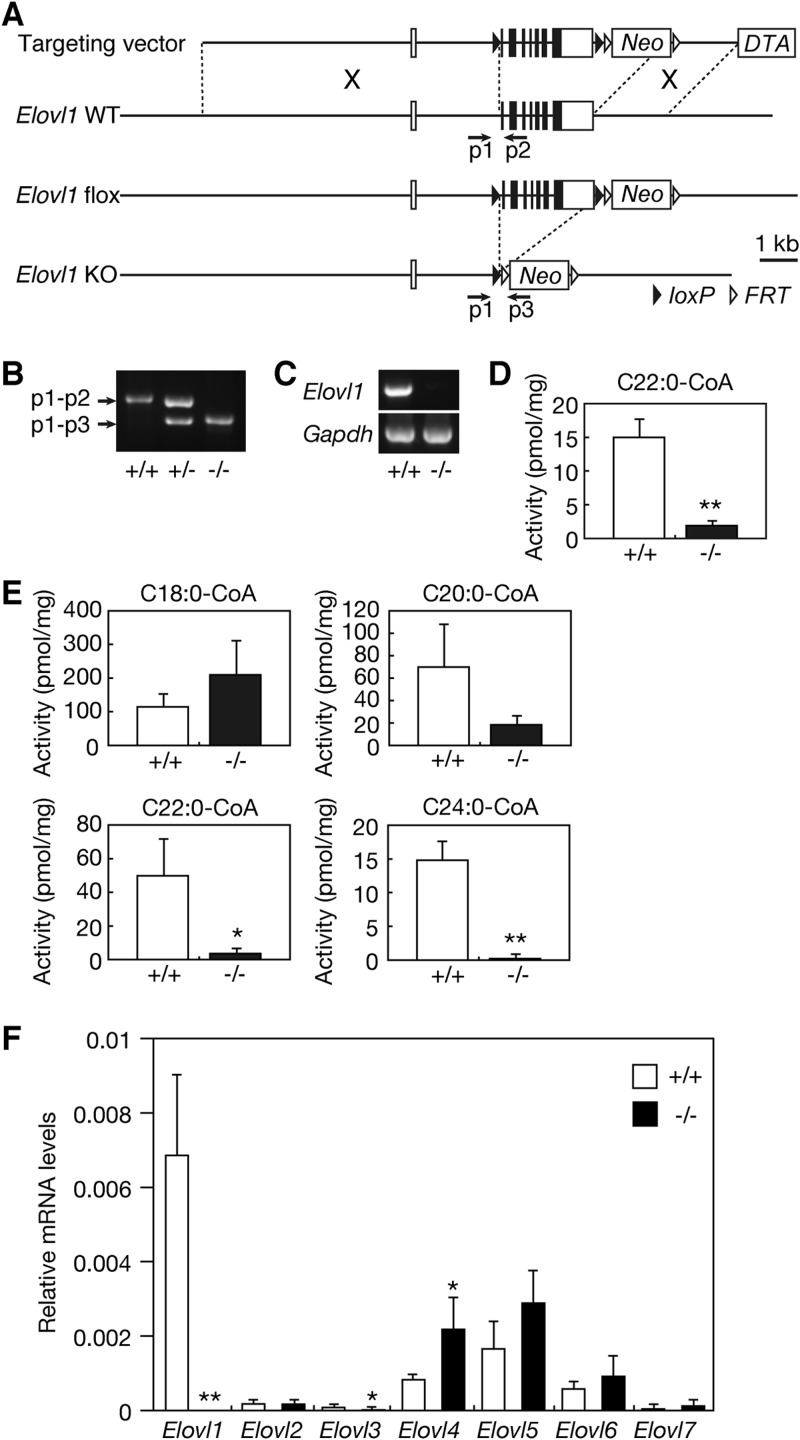
Fig 1.
Generation of Elovl1 knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the Elovl1 gene-targeting construct. In the targeting construct, exons 2 to 8 (2.4 kbp) of the Elovl1 gene are flanked by two loxP sequences, leaving an 8-kbp 5′-homologous region and a 2-kbp 3′-homologous region. Neo and DTA represent the positive selection marker, the neomycin resistance gene, and the negative selection marker, the diphtheria toxin A gene, respectively. Homologous recombination between the Elovl1 gene and the targeting construct yielded the Elovl1 flox allele. Crossing Elovl1+/flox mice with CAG-Cre mice produced Elovl1+/− mice. The positions of the primers (p1, p2, and p3) used for genomic PCR are depicted as arrows. KO, knockout. (B) Genomic DNAs prepared from the tails of Elovl1+/+, Elovl1+/−, and Elovl1−/− mice were subjected to PCR using primers p1, p2, and p3. The amplified fragments were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide. (C) Total RNAs were prepared from the skin of Elovl1+/+ and Elovl1−/− mice and subjected to RT-PCR using primers specific for the Elovl1 and Gapdh genes. The amplified fragments were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, followed by staining with ethidium bromide. (D) Total membrane proteins (50 μg) were prepared from the skin of Elovl1+/+ and Elovl1−/− mice and subjected to an in vitro FA elongase assay using 50 μM C22:0-CoA and 0.075 μCi [14C]malonyl-CoA (55 mCi/mmol; Moravek Biochemicals, Brea, CA) as the substrates. After a 30-min incubation at 37°C, lipids were subjected to methanolysis, extraction, separation by reverse-phase TLC, and detection using a BAS-2500 bioimaging analyzer (Fuji Photo Film, Tokyo, Japan). Values were calculated from the amounts of FA methyl ester products and represent the means ± standard deviations (SD) of three independent experiments. A statistically significant difference is indicated (**, P < 0.01; Student's t test). (E) Total membrane proteins (20 μg) were prepared from primary cultures of Elovl1+/+ and Elovl1−/− keratinocytes and subjected to an in vitro FA elongase assay using the indicated acyl-CoA (10 μM) and 0.075 μCi [14C]malonyl-CoA as the substrates. After a 60-min incubation at 37°C, lipids were saponified, acidified, extracted, and separated by normal-phase TLC, followed by detection using a BAS-2500 bioimaging analyzer. Values were calculated from the amounts of FA products and represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student's t test). (F) Total RNAs were prepared from the skin of Elovl1+/+ and Elovl1−/− mice. SYBR green-based real-time quantitative PCR was performed using primers specific for Elovl1, Elovl2, Elovl3, Elovl4, Elovl5, Elovl6, and Elovl7, and for Gapdh as an internal control. The expression level of each Elovl mRNA was calculated using a standard curve and normalized to that of Gapdh. Values presented are the amount of each Elovl mRNA relative to that of Gapdh and represent the means ± SD from eight independent reactions. Statistically significant differences compared to results for the Elovl1+/+ mice are indicated (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student's t test).