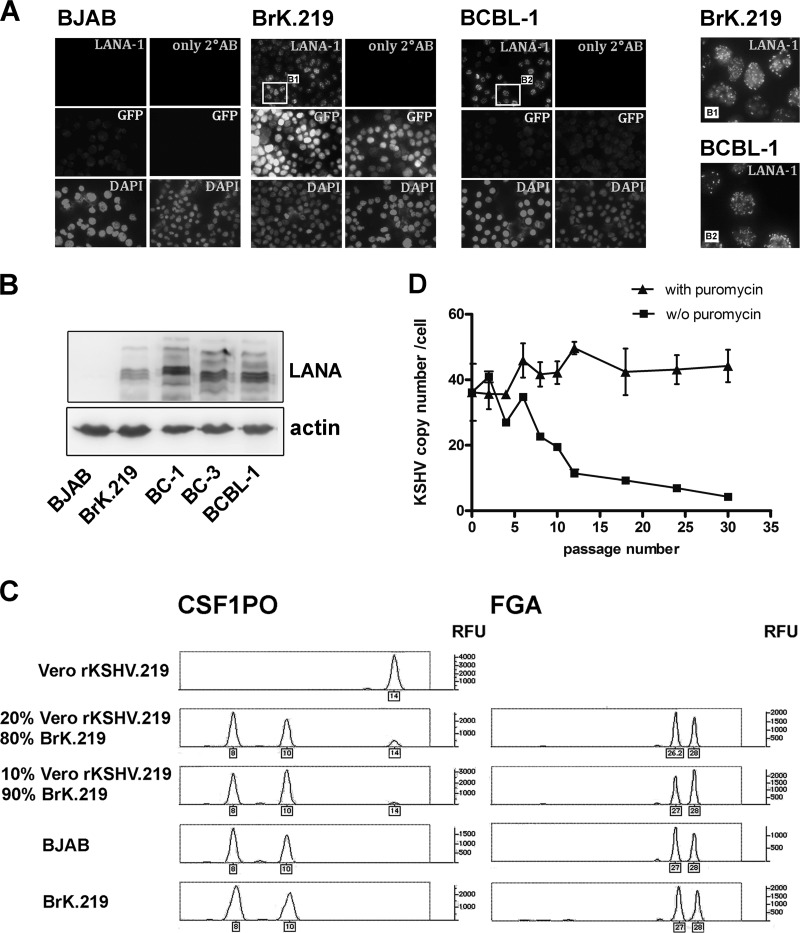
Fig 1.
Establishment of BrK.219 cells, LANA expression, and persistence of viral genomes. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of the latent viral nuclear antigen LANA was carried out in BrK.219 cells, the uninfected parental BJAB cell line, and the PEL cell line BCBL-1. Cells infected with rKSHV.219 express GFP constitutively. Samples were fixed, blocked, and incubated either with primary antibody against LANA, or without primary antibody, followed by a Cy5-conjugated secondary antibody. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole). Magnified images of the boxed regions B1 and B2 are shown on the right. (B) Expression of LANA shown by immunoblotting. (C) BrK.219 cells are BJAB-derived. BrK.219 cells established by coculture with rKSHV.219-infected Vero cells as described in Materials and Methods were analyzed using STR analysis for two gene loci, CSF1PO and FGA. The result indicates that BrK.219 cells and BJAB cells share the same genetic profile but differ from Vero cells. (D) Persistence of KSHV genomes in the presence or absence of puromycin. Samples were taken twice a week, and the number of KSHV genomes was measured by qPCR and normalized to CRP (a cellular gene) copy numbers.