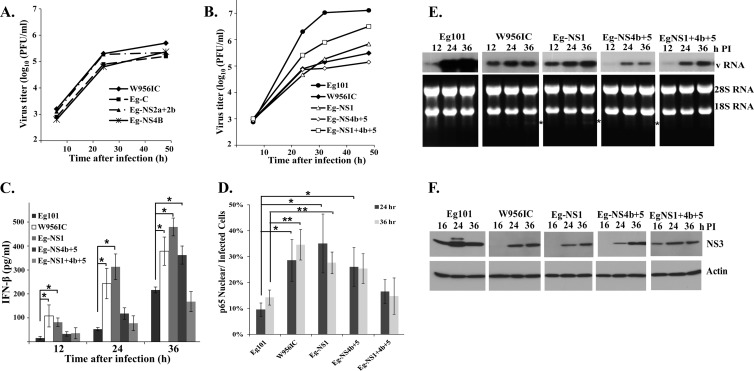
Fig 9.
Relative replication efficiency and extent of IFN-β induction by additional WNV chimeric viruses. (A and B) C3H/He MEFs were infected with Eg101 or W956IC or another chimera at an MOI of 1, the supernatants were collected at the indicated times after infection, and the viral titers were determined by plaque assay on BHK cells. The values shown are averages of duplicate titrations from two experiments. (C) The levels of IFN-β protein in supernatants from infected C3H/He MEFs were determined by ELISA. The values shown are averages from two or more independent experiments performed in duplicate. Bars represent ± standard deviations. Asterisks indicate values that were statistically significant (*, P < 0.05). (D) Quantification of the percentage of infected cells with nuclear p65 localization was done at the indicated times after infection. At least three fields for each condition were counted, and average values were plotted. Bars represent ± standard deviations. Asterisks indicate values that were statistically significant (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005). (E) Northern blot analysis of total cellular RNA from C3H/He MEFs infected with Eg101, W956IC, or another chimera. Cells were infected at an MOI of 1 for the indicated times. Total cell RNA (5 μg) was separated on a 1% denaturing agarose gel and transferred to a Hybond-XL membrane. The blot was hybridized to a 32P-labeled DNA probe specific for the 3′ untranslated region of the WNV genomic RNA. rRNA detected by ethidium bromide staining was used as a loading control. (F) C3H/He MEFs were infected with WNV Eg101, W956IC, or another chimera at an MOI of 1. At the indicated times after infection, cell lysates were prepared, and proteins were separated, transferred, and assayed by Western blotting using anti-WNV NS3 antibody. Actin was used as the loading control. The blots shown are representative of results obtained from three independent experiments.