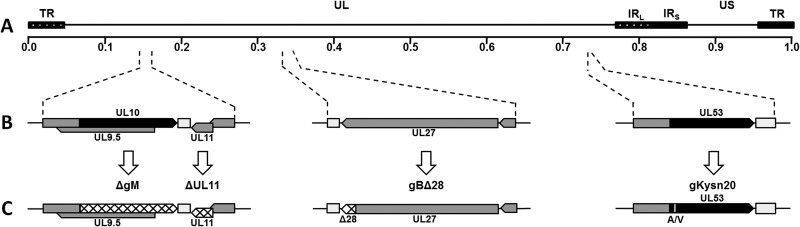
Fig 1.
Schematic representation of mutant viruses. (A) Prototypic arrangement of the HSV-1(F)-YE102 genome with the unique long (UL) and unique short (US) regions flanked by the terminal repeat (TR) and internal repeat (IR) regions. (B) Relative genomic positions and gene arrangements of targeted genes encoding the viral glycoproteins gB (UL27), gM (UL10), and gK (UL53) and membrane protein UL11. (C) Schematic representation of engineered mutations. Mutant viruses containing the ΔgM and ΔUL11 mutations were produced by changing the initiation codons of each gene (hatched regions). Mutant viruses containing gBΔ28 were produced by introduction of a stop codon causing truncation of gB by 28 amino acids (hatched region in gB). Mutant viruses containing gKsyn20 were produced by a point mutation (Ala to Val) at gK amino acid position 40 (white vertical line in gK).