Fig 4.
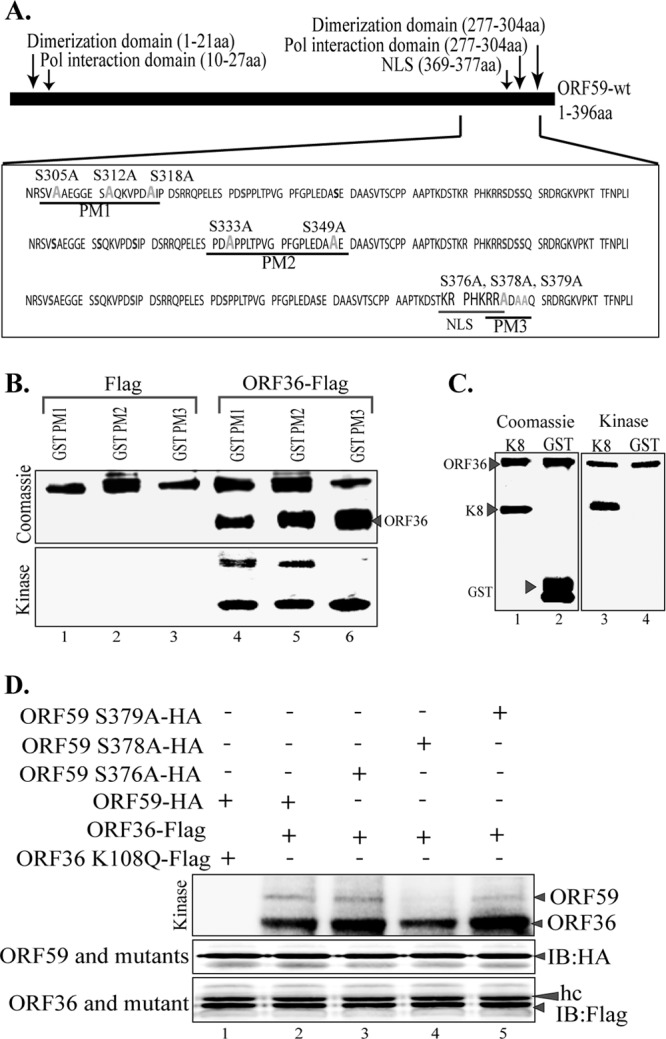
ORF36 phosphorylates ORF59 at Ser376, Ser378, and Ser379. (A) Schematic of ORF59 point mutants (PM1, PM2, PM3) used in the identification of specific phosphorylation targets by ORF36 kinase. The serine residues identified in the ProsKinase program as potential phosphorylation targets are marked in red. The serine residues mutated to alanines are marked in green. (B) In vitro kinase assay with ORF59 GST-fused point mutants. (Bottom) Autoradiography image of ORF59 PM1, PM2, and PM3 with the control Flag vector (lanes 1 to 3) and with immunoprecipitated ORF36-Flag (lanes 4 to 6). ORF59 PM3 was not phosphorylated by ORF36, which thus identified Ser376, Ser378, and Ser379 to be the specific sites of ORF36 phosphorylation. Lanes 4 to 6 show that autophosphorylation of ORF36 is essential for its kinase function. (Top) Proteins used in the kinase assay. Lanes 1 to 3, ORF59-GST PM1, PM2, and PM3 with Flag, respectively; lanes 4 to 6, PM1, PM2, and PM3 with ORF36 kinase, respectively. Lanes 4 to 6 of the Coomassie panel show the levels of ORF36 used for the in vitro kinase assay. (C) K8 was used as a positive control for ORF36 phosphorylation. (Left) Coomassie-stained gel of K8 (substrate) and GST, as a control; (right) phosphorylation of K8 as well as autophosphorylation of ORF36 but no phosphorylation of just GST. (D) ORF59 with serine 378 mutated to alanine lacks ORF36-mediated phosphorylation. Mutants with a single amino acid mutation at Ser376A (lane 3), Ser378A (lane 4), and Ser379A (lane 5) were immunoprecipitated and subjected to the kinase assay with ORF36. ORF59 with Ser378 mutated to A showed almost no phosphorylation (lane 4). The Ser379A mutant (lane 5) also had slightly reduced phosphorylation compared to that of Ser376A (lane 3) and wt ORF59 (lane 2). The kd mutant (ORF36 K108Q) was unable to phosphorylate ORF59 (lane 1). Immunoprecipitated ORF59 and its mutants were detected by anti-HA Western blotting (IB: HA). ORF36 and mutant were detected by anti-Flag Western blotting (IB: Flag). hc, heavy chain.
