Fig 2.
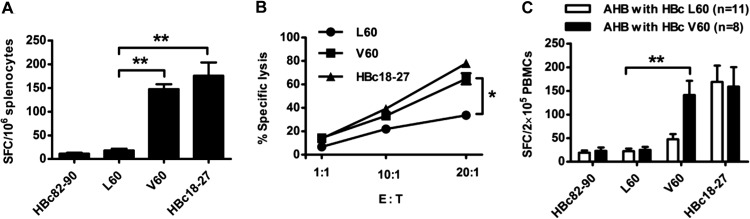
Detection of the HBc L60 peptide- and V60 peptide-specific CD8+ T cell response in HLA-A2.1/Kb mice and AHB patients. Female HLA-A2.1/Kb transgenic mice were immunized with a DNA prime/peptide boost regimen at weeks 1, 3, and 4. The HBc82-90 and HBc18-27 peptides served as negative and positive controls, respectively. Mice were sacrificed 1 week after the last immunization. (A) Fresh splenocytes (1 × 106) were stimulated with L60 peptide, V60 peptide, or HBc82-90 or HBc18-27 as negative and positive controls, respectively, and peptide-specific CTLs were detected by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. (B) 293T cells labeled with CFSE were transfected with pHBV1.3 or pHBV1.3-HBcL60V as target cells and mixed with L60-, V60-, or HBc18-27-stimulated splenocytes at different ratios: 1:1, 1:10, and 1:20. After 4 h, the mixed samples were stained with PI and analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. The data shown are the means ± SDs of five mice. E:T, effector-to-target cell ratio. (C) Detection of peptide-specific CTLs in AHB patients by ELISPOT assay. PBMCs (2 × 105/well) from patients infected with wild-type (HBcL60) or variant (HBcV60) virus were stimulated with L60 peptide, V60 peptide, or HBc82-90 or HBc18-27 as negative and positive controls, respectively, and analyzed by ELISPOT assay. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
