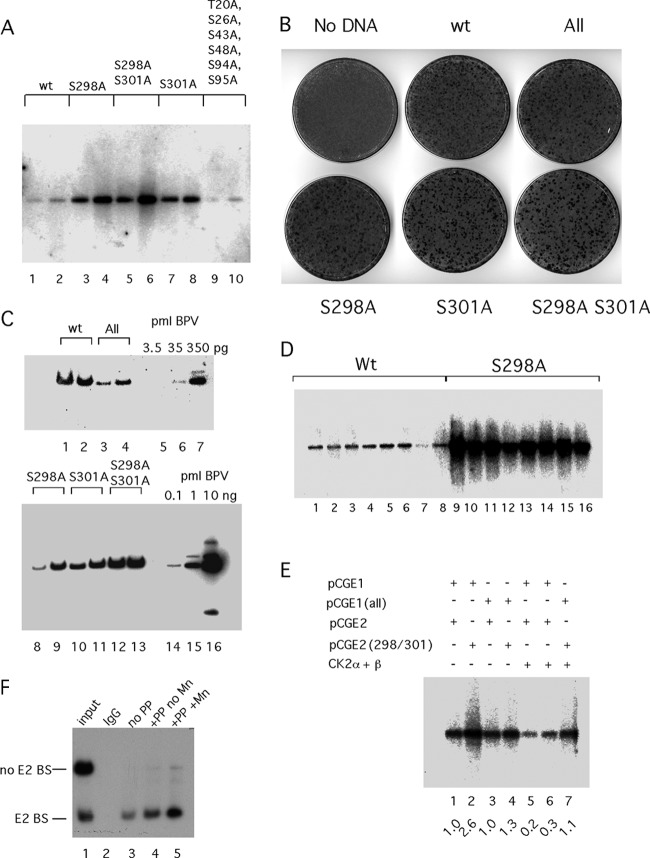
Fig 5.
Effects of E1 and E2 phosphorylation on viral DNA replication. (A) Viral DNA with mutations at S298A and S301A and the S298A S301A double mutant in E2 or with mutations at T20A, S26A, S43A, S48A, S94A, and S95A (All) in E1 was transfected into C127 cells, and time points were taken 4 and 5 days after transfection, harvested by alkaline lysis, and prepared for digestion with DpnI and EcoRI. After Southern transfer, the replicated DpnI-resistant viral DNA was detected by hybridization to a radiolabeled genomic BPV probe. (B) Morphological transformation assays were performed by transfecting the BPV genome into C127 cells using Fugene HD. Cells were fixed and stained with methylene blue after 2 weeks. (C) Transformed foci generated after transfection of C127 cells with the BPV genome containing phosphorylation mutations in E1 and E2 were picked and expanded into cell lines. Genomic DNA was generated and digested with the single cutter BstEII, fractionated by agarose gel electrophoresis, and analyzed by Southern blotting and hybridization with a 32P-labeled BPV probe. Cloned viral DNA was loaded as standards for quantitation. (D) Eight foci each from C127 cells transfected with the wt BPV genome or the S298A phosphorylation mutant were picked and expanded. Low-molecular-weight DNA was prepared from the individual clones and analyzed by Southern blotting and hybridization using a genomic BPV probe. (E) Transient replication assays were performed by transfecting an ori plasmid (11/12/X) together with expression vectors for wt E1 (pCGE1) or E1 with point mutations in the six CK2 phosphorylation sites (T20A, S26A, S43A, S48A, S94A, S95A) in the N-terminal domain (pCGE1 All) and wt E2 (pCGE2) or E2 with the point mutations S298A and S301A (pCGE2 298/301) into CHO cells by electroporation, as indicated. In lanes 5 to 7, expression vectors for CK2α and CK2β were cotransfected with the ori and the E1 and E2 expression vectors. Replicated, DpnI-resistant ori DNA was analyzed by Southern blotting and hybridization with a 32P-labeled probe. The hybridization signal was quantitated, and the relative level of replication in each lane is indicated. (F) Dephosphorylation of E2 expressed in COS-7 cells increases E2's DNA binding activity. An expression vector for E2 carrying an HA tag was transfected into COS-7 cells. Two days after transfection, cytoplasmic extracts were prepared and incubated with the monoclonal antibody 12CA5, which recognizes the HA tag and bound to protein G-Sepharose beads. The beads were divided into three equal parts: one part was treated with 100 U of the protein phosphatase lambda in the presence of Mn2+, one part was treated with 100 U of lambda phosphatase in the absence of Mn2+, and the third sample was left untreated. After being washed, the beads were incubated with two 32P-labeled DNA probes, one of which contained an E2 BS. The bound probes were dissociated from the beads and analyzed by PAGE.