Fig. 1.
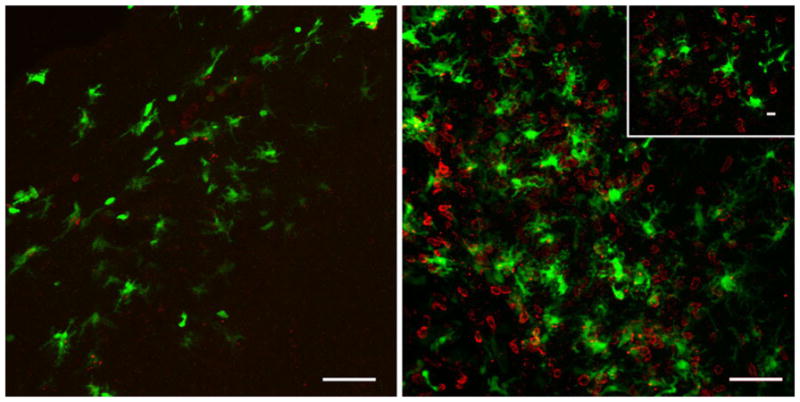
Putative DC within the brain can interact with CD4+ T lymphocytes following viral-induced neuroinflammation. Representative confocal Z-stack analysis of a VSV intranasally infected olfactory bulb at 4 (left) and 7 (right) days post-infection. CD11c/EYFP+ cells (green) are found throughout glomerular tissue richly populated with CD4+ T cells (red). Inset depicts a confocal section in which CD11c/EYFP+ cells are in physical contact with CD4+ T cells. Representative images from three experiments with an n =3; scale bar 50 μm (10 μm inset)
