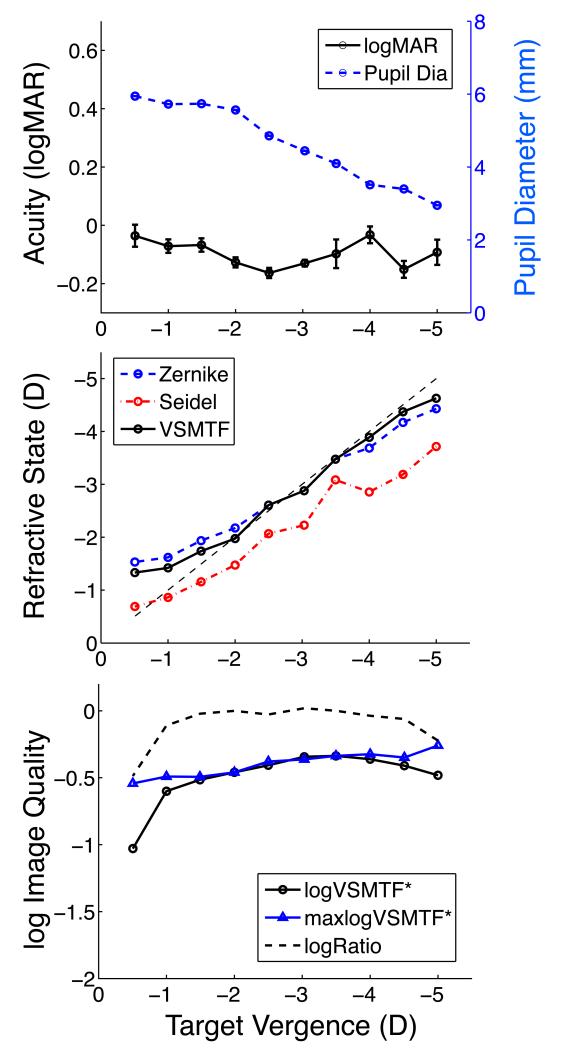
Figure 3.
Example of accurate accommodation and normal acuity for observer JM. Upper panel shows variation of binocular visual acuity (black line, left ordinate, symbol = mean, error bar = +/− 1 standard error of the mean) and pupil diameter (blue line, right ordinate) with target vergence. Large values of negative target vergence correspond to a near target. Middle panel shows absolute refractive state of the accommodating eye + spectacle system computed three ways as a function of target vergence. Dashed line indicates ideal focusing (optimum target vergence matches the physical target vergence). Lower panel shows absolute image quality (VSMTF*) for the measured wavefront (circles) relative to the maximum possible value (triangles) achieved by optimum focusing of the wavefront. Dashed curve is the ratio of VSMTF* to maximum VSMTF*. Ordinate for the bottom panel is logarithmic.