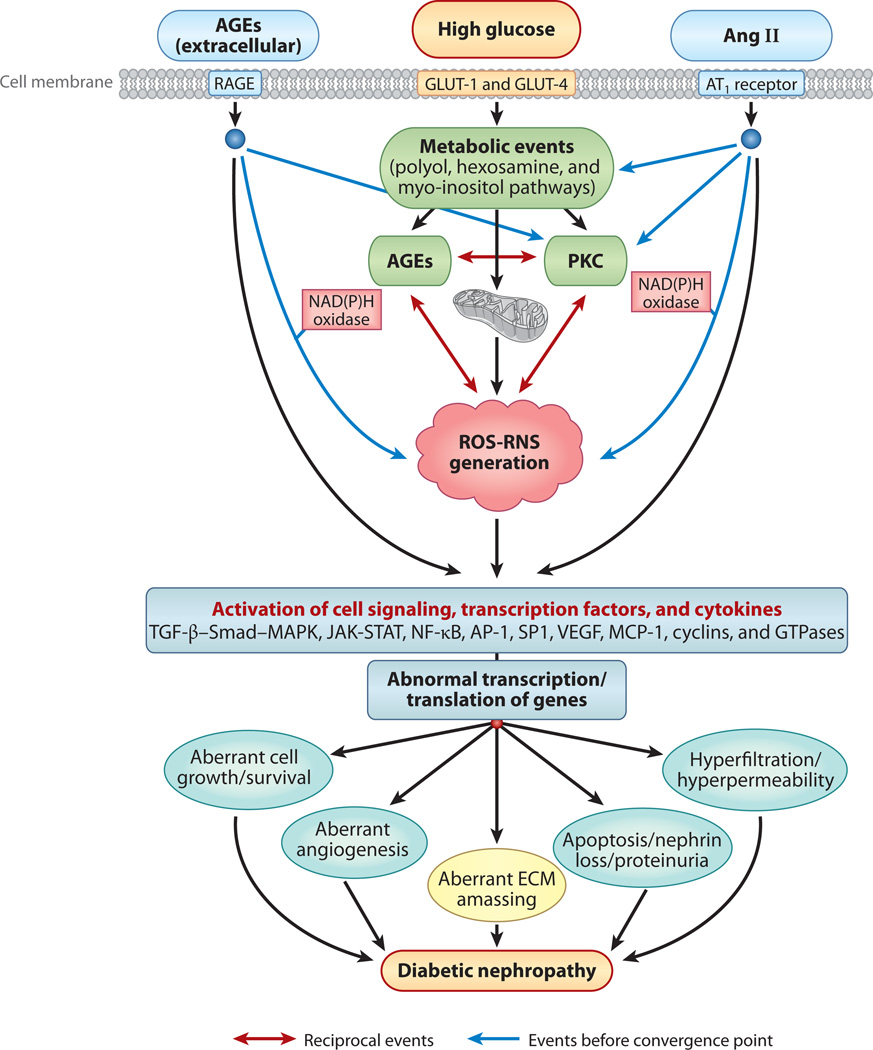
Figure 2.
An overview of different signaling events induced by exposure of renal cells to high glucose concentrations, with resulting altered expression of various genes and cellular abnormalities leading to diabetic nephropathy. The schematic drawing also highlights the hypothetical cross talk between AGE-RAGE (advanced glycation end product–receptor for AGE) and the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and the reciprocal-cyclical modulation of the interactions among AGEs, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and protein kinase C (PKC), with ROS as the central mediator. Abbreviations: Ang II, angiotensin II; AP-1, activator protein 1; AT1, Ang II receptor; ECM, extracellular matrix; GLUT, glucose transporter; JAK-STAT, Janus kinase–signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; NF-κB; nuclear factor κB; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.