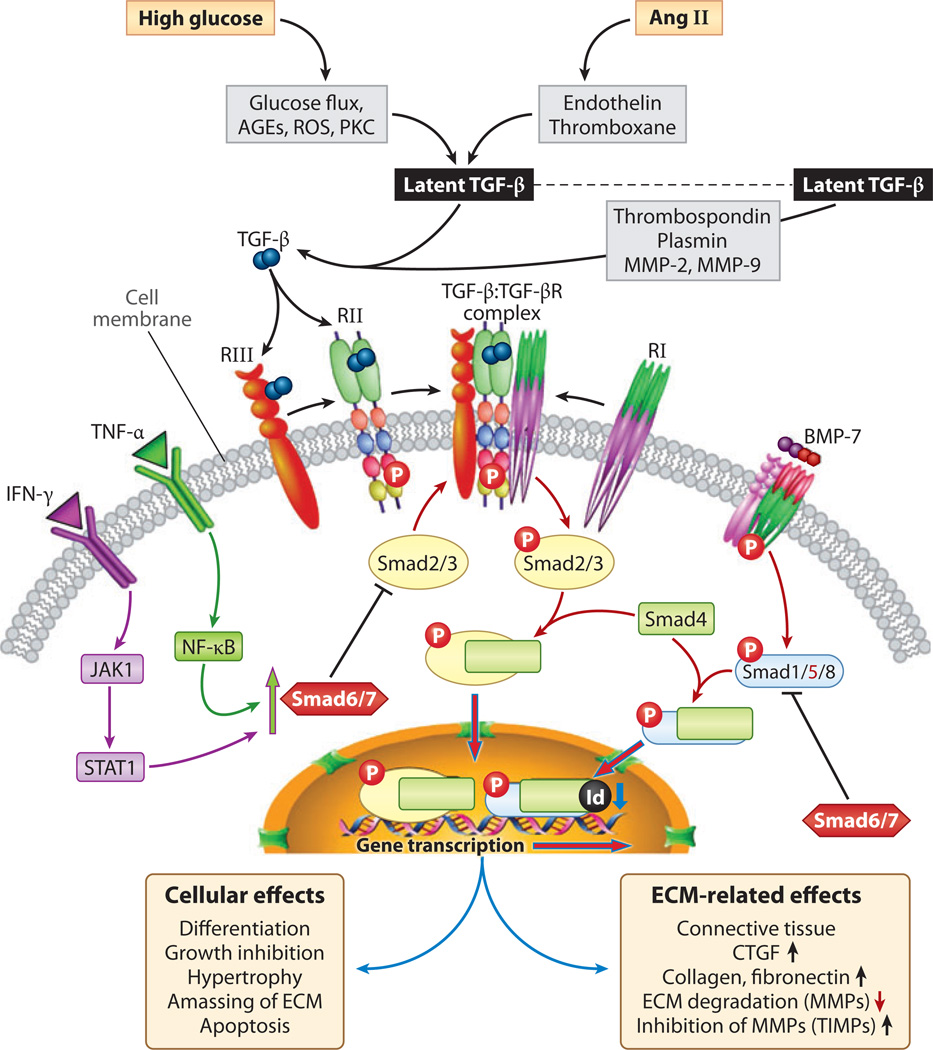
Figure 7.
Schematic depicting transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP-7) signaling. Activation of latent TGF-β by glucose, advanced glycation end products (AGEs), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and angiotensin II (Ang II) leads to the generation of TGF-p, which binds first to type II and III serine/threonine kinase receptors with recruitment and phosphorylation of type I. Activated heteromeric complex interacts with Smad2/3 and co-Smad4. Smad2/3 are inhibited by Smad6/7, which are induced by tumor necrosis factor α. (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) signaling. The Smad2/3/4 complex translocates into the nucleus to initiate transcription of various extracellular matrix (ECM) genes and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF). BMP-7, however, activates Smad1/5/8, which bind to co-Smad4 and, upon translocation into the nucleus, induce Id proteins that inhibit differentiation and DNA binding of some of the transcription factors, thereby opposing the action of TGF-β. Abbreviations: JAK, Janus kinase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB; nuclear factor κB; PKC, protein kinase C; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase.