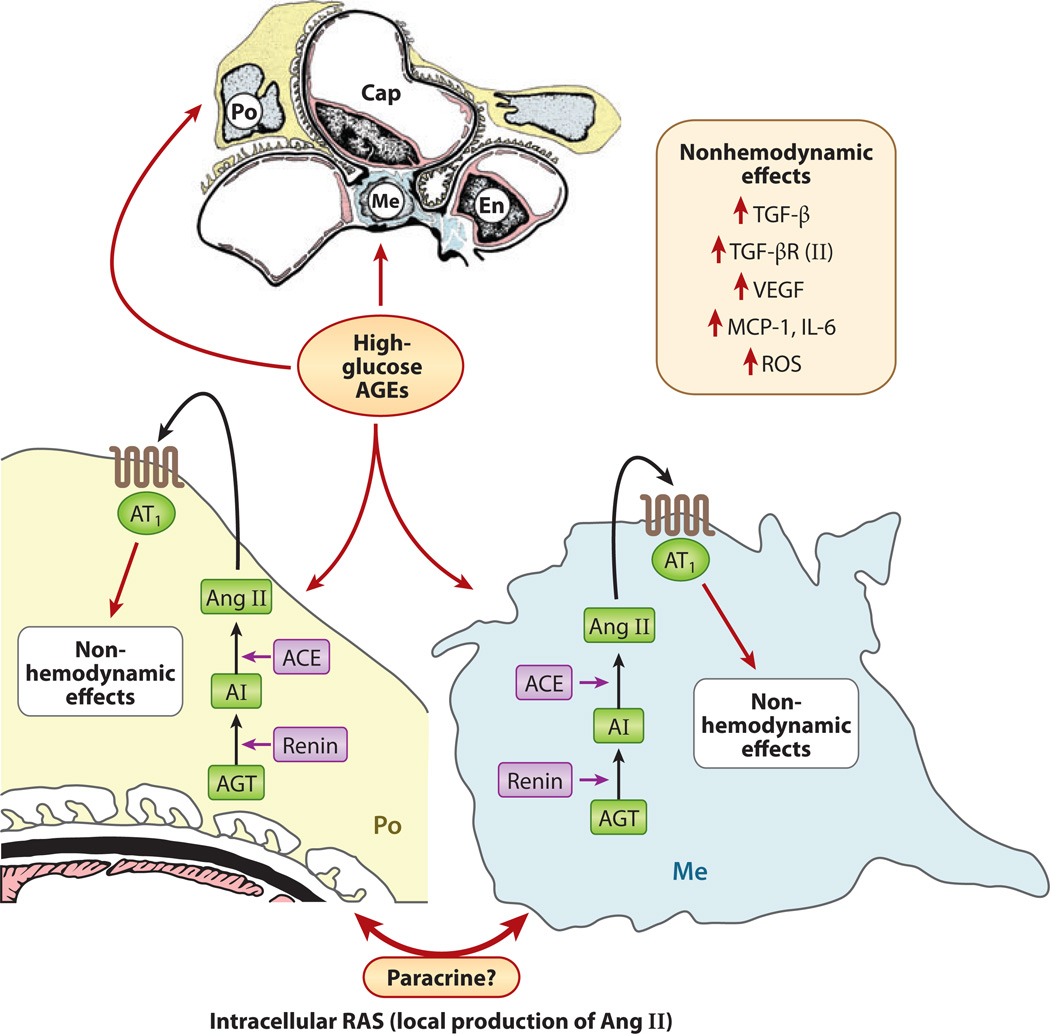
Figure 9.
Schematic drawing depicting local glomerular activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) by glucose flux and advanced glycation end products (AGEs). Both podocytes (Po) and mesangial cells (Me) of the glomerulus express angiotensin II (Ang II) receptors (AT1). Angiotensin I (AI) is synthesized from angiotensinogen (AGT) by the action of renin. AI is converted into angiotensin II (Ang II) by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Ang II, upon binding to its AT1 receptor, induces various nonhemodynamic effects, including increased activity of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and expression of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Abbreviations: Cap, capillary; En, endothelium; IL-6, interleukin-6; TGF-βR, TGF-β receptor.