Figure 1.
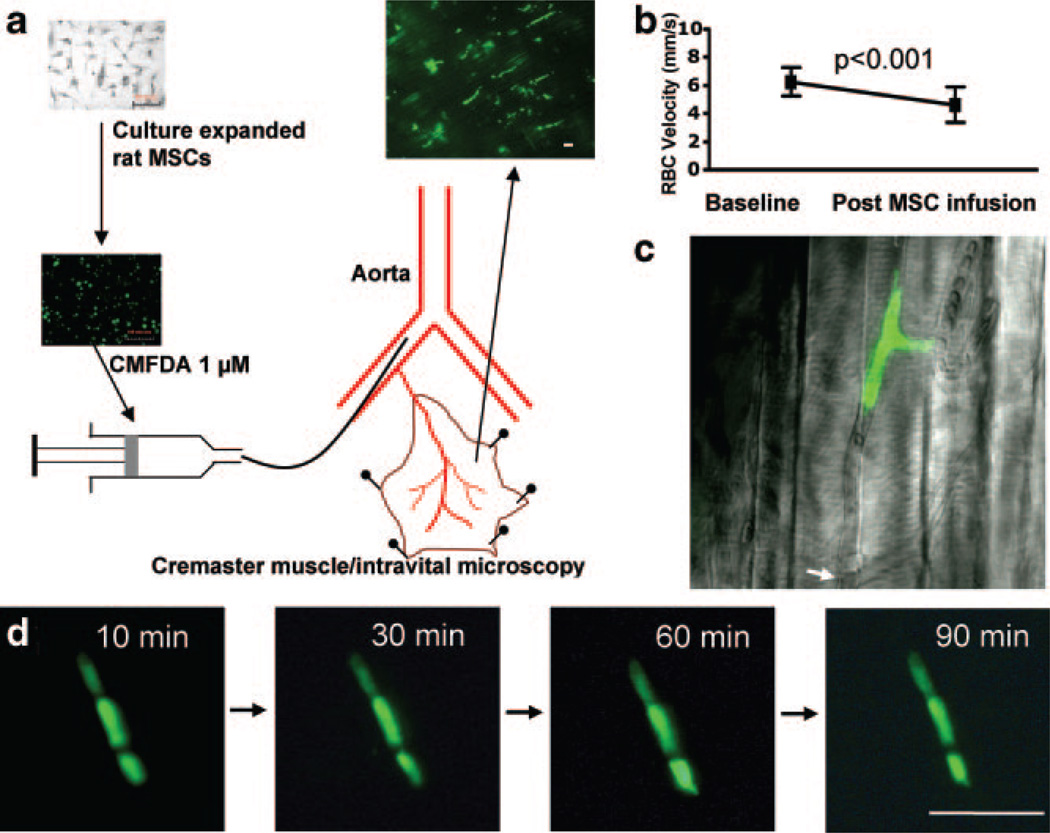
Rheological effects of intraarterially delivered MSCs. a, MSCs fluorescently labeled with CMFDA were injected above the origin of the cremaster artery, leading to diffuse precapillary cell entrapment. b, Microvascular plugging significantly decreased the RBC velocity in the feeding arteriole. c, High magnification of MSCs arrested in a microvessel with interruption of flow (arrow indicating the flow divergence point; see supplemental Video 1). d, Three entrapped MSCs observed for up to 90 minutes: no morphological changes suggestive of extravascular migration. Scale bar = 100 µm.