Fig. 7. Blocking L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels attenuated γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced increases of [Ca2+]i.
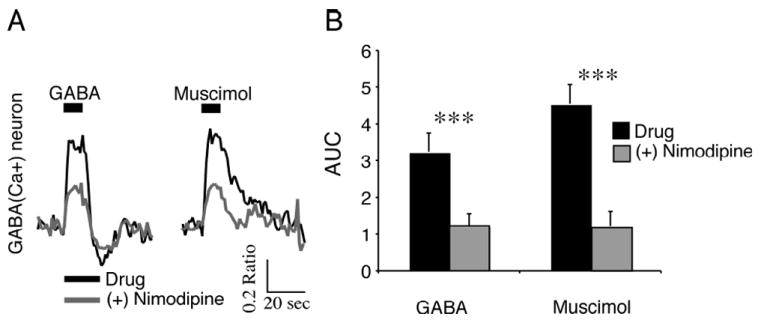
(A) Ca2+ responses induced by GABA (200 μm, 10 s) or muscimol (50 μm, 10 s) in a GABA(Ca+) neuron during the day before and after nimodipine (20 μM) application. Both GABA- and muscimol-induced Ca2+ transients were attenuated. (B) Nimodipine attenuated GABA- and muscimol-induced Ca2+ transients in GABA(Ca+) neurons. Data are the mean ± SEM of the area under the curve (AUC; Ca2+ ratio/s over 0-10 s of GABA treatment) for GABA(Ca+) (n = 30, t29 = 6.03 GABA, t29 = 10.6 muscimol, ***P < 0.00001) SCN neurons.
