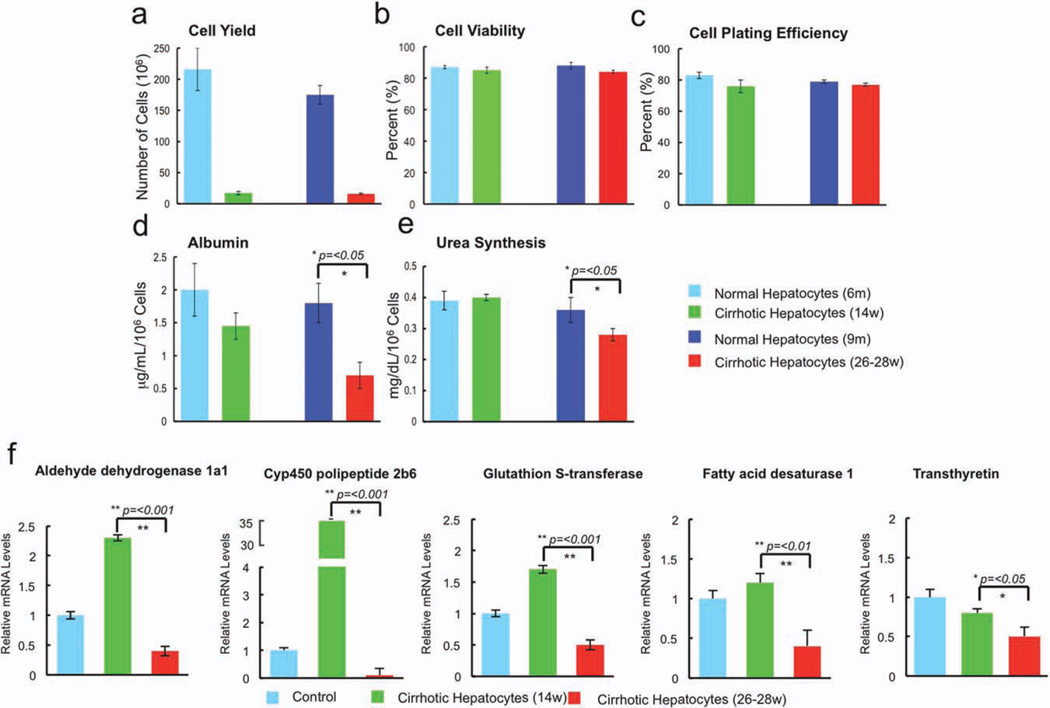
Fig. 2.
Yield after isolation and functional characteristics of cells recovered from normal control livers, early cirrhotic livers, and advanced cir-rhotic livers. (a) The yield of cells recovered by collagenase digestion from cirrhotic livers was significantly lower than that recovered from age-matched controls and was approximately 5% of that recovered from control livers. (b,c) Cell viability (b) and cell plating efficiency (c) were not statistically different among groups. (d,e) Hepatocytes derived from control rats and rats with compensated cirrhosis secreted equal amounts of albumin (d) and urea (e), whereas hepatocytes from the livers of cirrhotic rats with liver failure secreted significantly less of each (P < 0.05). (f) A cohort of liver-specific genes was examined using qPCR and documented up-regulation in early cirrhosis followed by significant down-regulation (compared with control) in late cirrhosis of CYP450 and metabolic enzyme gene expression in hepatocytes derived from the livers of rats with decompensated cirrhosis: ADH1a1, CYP4502b9, GST, FADS1, and transthyretin.