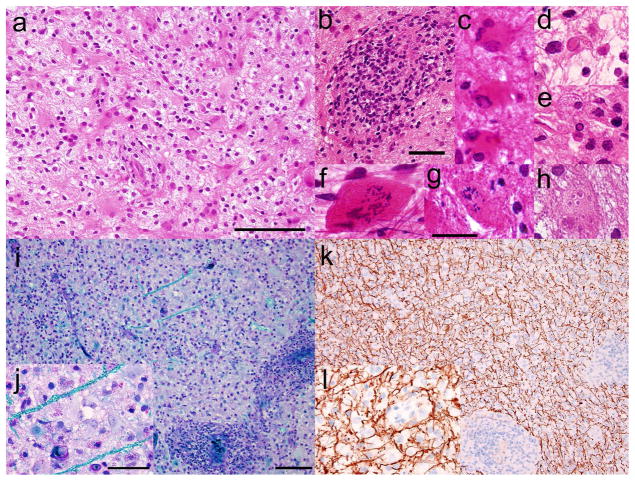
Fig. 2.
Stereotactic biopsy of right frontal lobe lesion. a Haematoxylin and eosin staining of paraffin sections shows pale but hypercellular brain tissue with reactive gliosis, foamy macrophages, neuroaxonal spheroids, and b perivascular infiltrates of benign lymphocytes. c Some reactive astrocytes are multinucleated. d,e Rare nuclei show glassy eosinophilic intranuclear bodies and marginated chromatin, suggestive of viral inclusions. Granular mitoses and cells with micronuclei (Creutzfeldt cells) are present in f cytological smear, g frozen section, and h paraffin sections. i Luxol-fast blue/Periodic acid Schiff preparations show severe myelin loss, j highlighting rare remaining myelinated axons in turquoise; k,l in contrast, immunohistochemistry for neurofilament protein, applied to the same tissue and viewed at the same magnifications, highlights abundant relatively preserved axons, indicative of a demyelinating process. Scale bars: a=100 μm; b=50 μm; g=25 μm (applies to c –h); i=100 μm (applies also to k); j=50 μm (applies also to l)