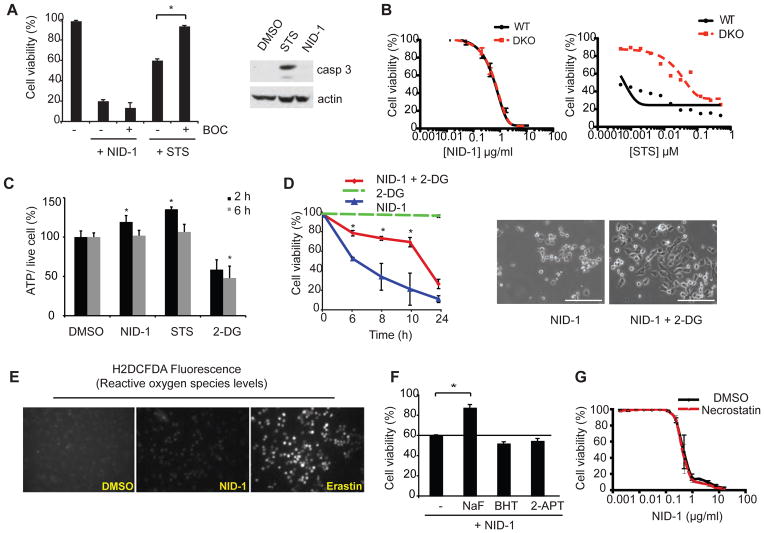
Fig. 2.
NID-1 induces an active, non-apoptotic cell death. (A) BJeLR cells were treated with NID-1 (10 μg/ml) or staurosporine (STS, 0.5 μM) alone or in combination with BOC (50 μM). Cell viability was assayed after 8 h (NID-1) or 20 h (STS) using the trypan blue dye-exclusion assay (left panel), * (p<0.05). Western blot of cleaved caspase 3: cells were treated with vehicle (DMSO), STS (0.5 μM) or NID-1 (5 μg/ml) and harvested after 4 h, and subjected to western blot for cleaved caspase 3. Actin was used as a loading control (right panel). (B) Dose-response for NID-1 and STS in WT MEFs and in isogenic bax−/−, bak−/− double knockout (DKO) MEFs. Viability was measured by Alamar blue assay 48 h after treatment. (C) ATP levels were determined following 2 and 6 h treatments with NID-1 (2 μg/ml), staurosporine (STS, 0.1 μM) and 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG, 5mM) and compared to DMSO control; * (p<0.05) (D) BJeLR cells were either pretreated with 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG, 5 mM) for 2 h, or left untreated, and then treated with NID-1 (10 μg/ml). Cell viability was determined using the trypan blue dye-exclusion assay, * (p<0.05, left panel). Data is representative of two independent experiments. Phase contrast images of NID-1 and NID-1 + 2-DG (5 mM) treated cells after 8 h. Scale bar, 200μm (right panel). (E) Reactive oxygen species were detected using H2DCFDA after 6 h of treatment with NID-1 (10 μg/ml), or erastin (10 μM), and compared to DMSO-treated control cells. (F) Cells were left untreated or pretreated with the various antioxidants (butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT, 150 μM) or 2-acetylphenothiazine (2-APT, 10 μM)) for 2 h before NID-1 (10 μg/ml) treatment. Sodium flouride (5 mM) was a positive control. Cell viability was determined using the trypan blue dye-exclusion assay, * (p<0.05). (G) BJeLR cells were treated with dose dilution of NID-1 alone or in combination with necrostatin-1 (5 μg/ml) and viability was determined by an Alamar Blue assay. Experiments are representative of at least 2 independent experiments.