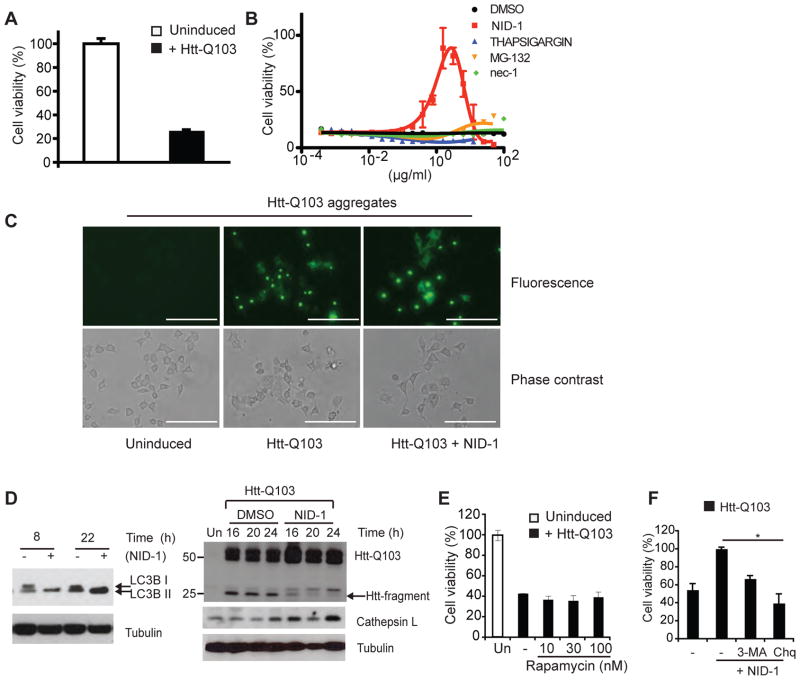
Fig. 7.
NID-1 suppresses mutant-huntingtin-induced cell death. (A) PC12 cells were un-induced or induced to express htt-Q103. Cell viability was determined 48 h after induction of mutant htt expression using the Alamar blue assay. Data represent the mean ± S.D. of an experiment performed in triplicate is representative of three independent experiments. (B) PC12 cells were induced to express htt-Q103 and treated with a dose-dilution of indicated compounds. Cell viability was determined 48 h later as in (A). Data represent the mean ± S.D. of an experiment performed in triplicate. The rescue by NID-1 was confirmed in three independent experiments. (C) PC12 cells were un-induced or induced to express mutant htt-GFP fusion protein and then treated with NID-1 (1 μg/ml) or DMSO. Htt-Q103 aggregates were visualized using fluorescence microscopy after 15 hr of treatment. Scale bar = 200 μm. (D) PC12 cells expressing mutant htt-Q103 were incubated with control (DMSO) or NID-1 (1 μg/ml), harvested at the times indicated, and levels of indicated proteins were analyzed by western blotting. Uninduced (Un) cells were controls for lack of htt-Q103 expression. (E) PC12 cells were uninduced or induced to express htt-Q103 and treated with a dose-dilution of rapamycin. Cell viability was determined 30 h later. The results represent the mean ± S.D. of an experiment performed in duplicate and is representative of 2 independent experiments. (F) PC12 cells were untreated or pretreated with 3-MA (5mM) or chloroquine (Chq, 15 μM) for 15 h. Cells were then treated with NID-1 (1μg/ml) and htt-Q103 was induced. Cell viability was determined 30 h after induction and viability of NID-1 treated cells was arbitrarily set as 100% (*, p< 0.05, student’s t-test). The results represent the mean ± S.D. of an experiment performed in duplicate and is representative of 2 independent experiments.