Figure 5. WAVE/SCAR and Arp2/3 are required for endosome maturation in coelomocytes.
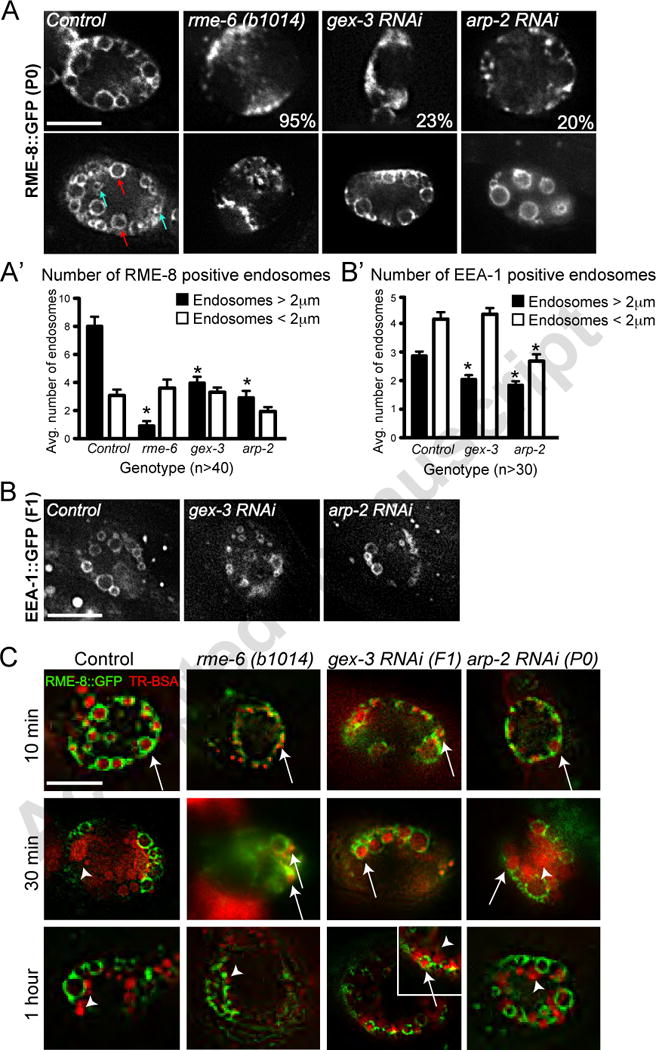
A. Effects of gex-3 and arp-2 on RME-8::GFP enrichment in coelomocytes. The top panels show coelomocytes with dramatically reduced RME-8::GFP-positive endosomes, similar to the effect of rme-6 loss. Percentages indicate number of animals with the strongest endosome defects. Bottom panels show coelomocytes with less severe defects. Arrows indicate small (< 2m, blue) and large (> 2μm, red) endosomes. A’: Quantitation of small and large endosomes.
B.,B’ Effects of gex-3 and arp-2 on EEA-1::GFP enrichment in coelomocytes.
C. Effects of gex-3 and arp-2 on transport into and out of RME-8::GFP-positive endosomes. RME-8::GFP animals were injected with TR-BSA, in the body cavity near the head, followed by incubation of the animals for 10, 30 and 60 minutes. Transport of TR-BSA into and out of the RME-8::GFP-positive endosomes was monitored. For comparison, the RAB-5 GEF RME-6 strongly delays transport through endosomes (Sato et al., 2005) with no accumulation in RME-8 ::GFP-positive endosomes at 30 minutes. Arrows and arrowheads indicate RME-8 positive endosomes filled with TR-BSA, and TR-BSA that has exited the endosomes, respectively. Scale bars = 10 μm. Error bars show standard error of the mean (SEM). Asterisks indicate statistical significance, p < 0.05.
