Fig. 3.
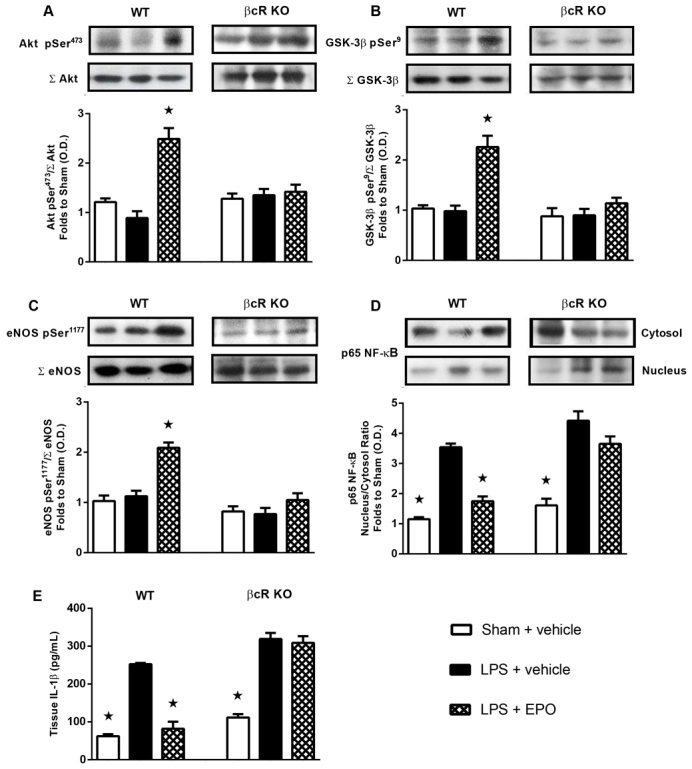
Effect of erythropoietin (EPO) on signalling pathways and IL-1β expression in the hearts of wild-type and β-common receptor knockout (βcR KO) mice with endotoxemia. Mice received either lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 9 mg/kg i.p.) or vehicle (5 ml/kg 0.9% saline i.p.). At 1 hour after induction of endotoxemia, mice were treated either with EPO (1000 IU/kg s.c.) or vehicle (10 ml/kg 0.9% saline s.c.). Densitometric analysis of the bands is expressed as relative optical density (O.D.) of (A) Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 (pSer473), corrected for the corresponding total Akt (ΣAkt) content and normalized using the related sham band, (B) glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β phosphorylation at Ser9 (pSer9), corrected for the corresponding total GSK-3β (ΣGSK-3β) content and normalized using the related sham band, (C) endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation at Ser1177 (pSer1177), corrected for the corresponding total eNOS (ΣeNOS) content and normalized using the related sham band, (D) nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65 subunit levels in both cytosolic and nuclear fractions and expressed as a nucleus:cytosol ratio, and (E) IL-1β expression in heart tissue of endotoxemic mice. Each immunoblot is from a single experiment and is representative of four separate experiments. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. for n number of observations. ★P<0.05 versus LPS + vehicle.
