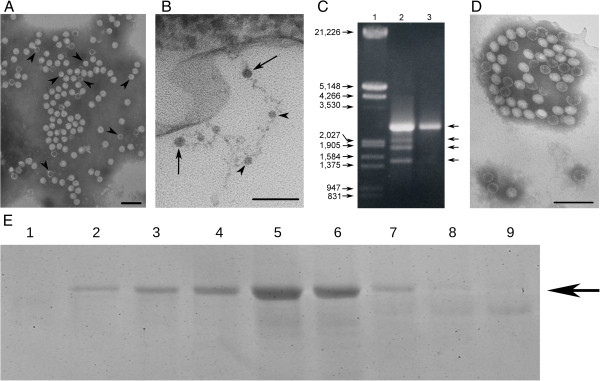
Figure 3.
Structural characterization of mycoviruses that infect to B. cinerea CCg378. (A) Electron micrograph of mycoviruses from B. cinerea CCg378 present in gradient fraction 5. Arrowheads indicate the position of 23-nm viral particles. (B) Ultrathin section of B. cinerea CCg378 mycelium containing viral particles. Arrows and arrowheads indicate the position of some mycoviruses of 32 and 23 nm in diameter, respectively. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of dsRNAs from B. cinerea CKg54vi378. Lane 1, lambda DNA/EcoRI + HindIII marker; lanes 2 and 3, dsRNAs from B. cinerea CCg378 and B. cinerea CKg54vi378 purified by CF11-cellulose chromatography, respectively. The numbers on the left indicate molecular sizes expressed in base pairs (bp). The arrows on the right indicate the position of dsRNAs. (D) Electron micrograph of mycoviruses from B. cinerea CKg54vi378. (A) and (D) Negative staining with 2% (w/v) potassium phosphotungstate, pH 7.0. The bar marker in (A), (B) and (D) represents 100 nm. (E) Polypeptide profile of gradient fractions 1–9 of particulate material obtained from B. cinerea CKg54vi378. The arrow on the right indicate the migration position of the major polypeptide.