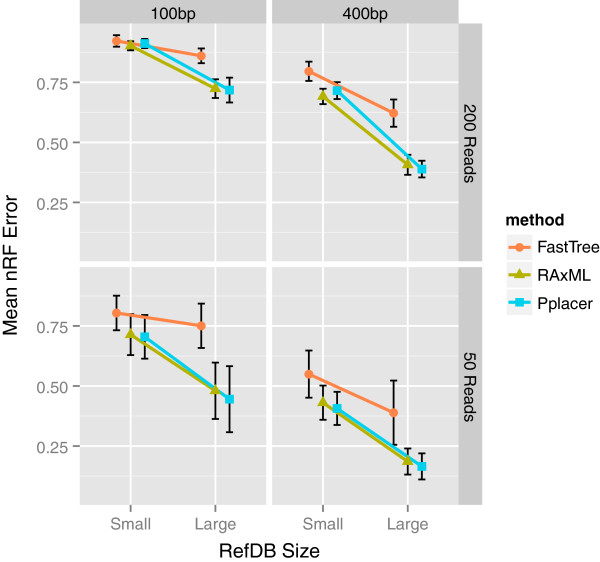
Figure 2.
Read-tree topological error varies with reference database size, read length, and number of reads. Mean topological error (nRF) varies widely from the most challenging scenario, where the reads are short and there is a relatively large number of reads (upper left), to the inverse scenario (lower right). It is inversely related to both reference database size and read length, and grows with the number of reads. RAxML and pplacer appear to take better advantage of the larger reference database (i.e., the slope of the corresponding line is steeper) than FastTree. In each panel, the nRF measure is averaged over 30 simulations for each combination of simulation parameters. Vertical error bars show a standard deviation above and below the mean. Data for rpoB family are shown; trends were similar across gene families tested (Additional file 2: Figure S1).