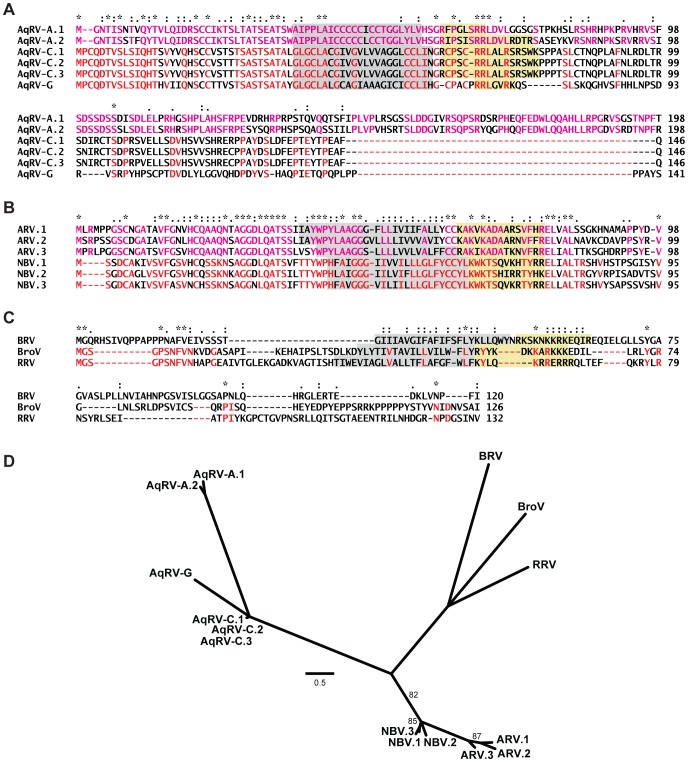
Figure 4. Comparisons of aqua- and orthoreovirus FAST proteins.
(A) MAFFT alignment of aquareovirus FAST proteins in Clustal format. Residues conserved among AqRV-A isolates in this figure are colored magenta; residues conserved among AqRV-C and AqRV-G isolates are colored red. (B) MAFFT alignment of orthoreovirus ARV and NBV FAST proteins in Clustal format. Residues conserved among ARV isolates in this figure are colored magenta; residues conserved among ARV isolates are colored red. (C) MAFFT alignment of orthoreovirus BRV, BroV, and RRV FAST proteins in Clustal format. Residues conserved in BroV and RRV are colored red. In A–C, TMDs predicted by TMHMM are background-shaded in gray; polybasic clusters following the TMDs are background-shaded in yellow. (C) Maximum-likelihood (PhyML 3.0) unrooted phylogram of aqua- and orthoreovirus FAST proteins. Program-estimated values for invariant proportion and gamma shape parameter were 0.007 and 3.598, respectively. Branches with support values ≥90% are not labeled, and those with support values <50% are collapsed into polytomies. AqRV-A.1 is Scophthalmus maximus reovirus (see Table S1) and AqRV-A.2 is Atlantic salmon reovirus Canada/2009 (GenBank accession no. ACN38055); AqRV-C.1 is Golden shiner reovirus (see Table S1), AqRV-C.2 is Grass carp reovirus 873 (GenBank accession no. AAM92738), and AqRV-C.3 is Channel catfish reovirus 730 (GenBank accession no. ADP05119); ARV.1 is strain 176 (see Table S1), ARV.2 is turkey reovirus strain NC/98 (GenBank accession no. ABL96273), and ARV.3 is Stellar sea lion reovirus (GenBank accession no. AED99910); NBV.1 is Nelson Bay virus (see Table S1), NBV.2 is Pulau virus (GenBank accession no. AAR13231), and NBV.3 is Xi River reovirus (GenBank accession no. ADE40974). For the other viruses shown in this figure, see Table S1.