Figure 11. Testing for the interaction between the Mod(mdg4)-67.2 and Zeste proteins.
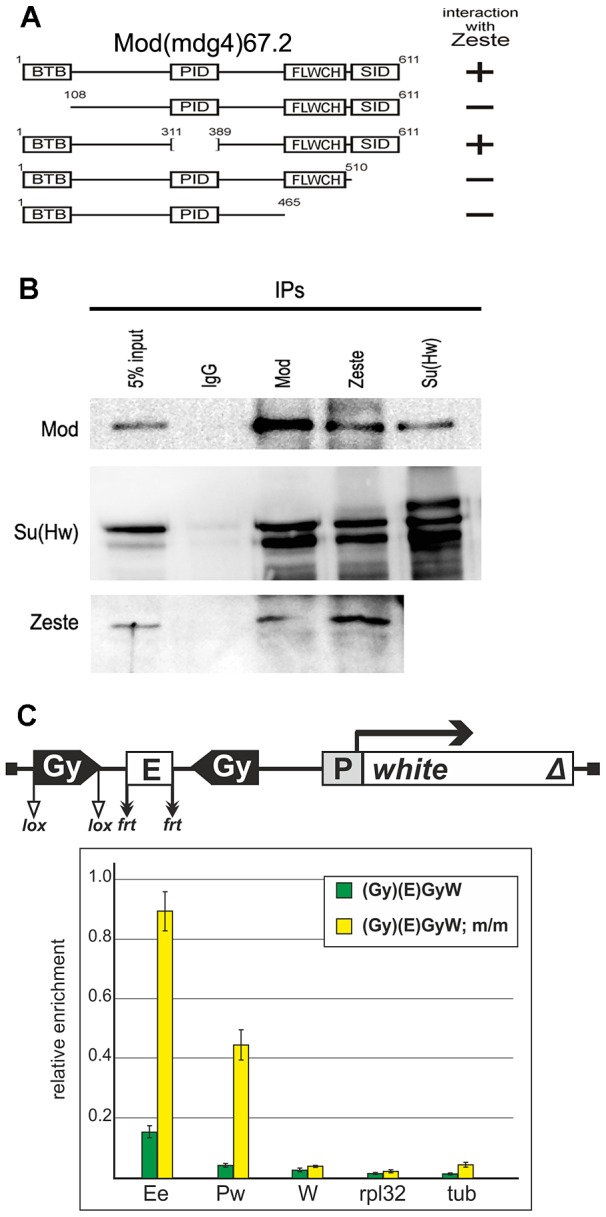
(A) Summary of interactions between Mod(mdg4)-67.2 and Zeste in the yeast two-hybrid assay. Schemes show the structure of the full-length Mod(mdg4)-67.2 and its deletion derivatives, indicating the main domains of this protein. Plus and minus signs refer to a relatively strong interaction and the absence of interaction, respectively. Different fragments of Mod(mdg4)-67.2 were individually fused to the C-terminus of the GAL4 activating domain and tested for the interaction with Zeste fused to the C terminus of GAL4 DNA binding domain. All Mod(mdg4) fragments were tested for the absence of interaction with GAL4 DNA binding domain alone. (B) Nuclear extracts from Drosophila S2 cells were immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific for the indicated proteins (with preimmune IgG used as a negative control), and the immunoprecipitates (IPs) were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of Mod(mdg4)-67.2 (designated Mod), Su(Hw) and Zeste proteins. (C) The results of ChIP (percentage of input DNA normalized relative to the endogenous positive binding site for Zeste from the Ubx promoter region) of specified chromatin regions with antibodies to Zeste in the transgenic construct. Analysis was performed with wild-type and mod(mdg4)u1/mod(mdg4)u1 (m/m) pupae carrying the transgenic construct. Error bars indicate standard deviations of quadruplicate PCR measurements. Other designations are as in Figure 1 and 9.
