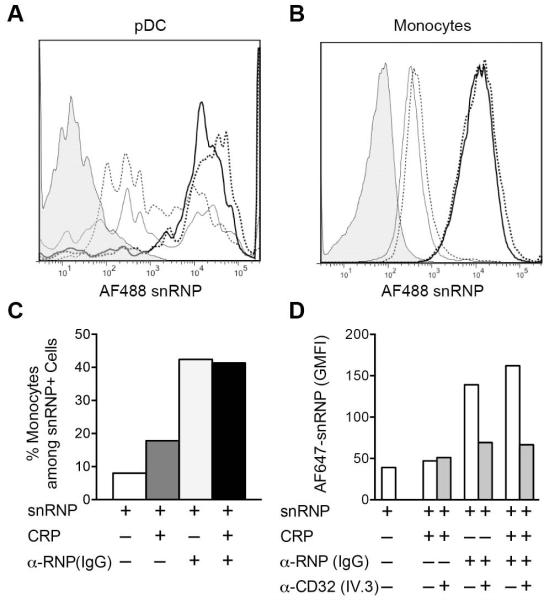
Figure 4.
CRP does not block IC binding to FcγRIIA on monocytes or pDC. PBMC were incubated for 1 h on ice with AF488 or AF647 snRNPs (5 μg/ml), CRP (200 μg/ml) and α-U1 RNP (200 μg/ml IgG). Cells were stained for monocyte (CD14) and pDC (CD123, CD303) markers, and analyzed by flow cytometry. A and B. Cells from each treatment group were gated on pDC (A) or monocytes (B) and analyzed for AF488 snRNPs binding. Histograms represent the following treatments: untreated cells (shaded); snRNPs only (light dotted line); CRP + snRNPs (light solid line); α-U1 RNP (IgG) + snRNPs (heavy dotted line); CRP + α-U1 RNP (IgG) + snRNPs (heavy solid line). C. AF488 snRNPs positive cells were gated and the percent CD14+ monocytes was determined for the different treatments. D. Inhibition of AF647 snRNPs binding to cells by anti-FcγRIIa blocking mAb IV.3. Cells were incubated with AF647 snRNPs (5 μg/ml), CRP (200 μg/ml) and α-U1 RNP (200 μg/ml IgG) for 60 min on ice in the presence and absence of 5 μg/ml anti-FcγRIIa blocking antibody. snRNPs binding is shown as the geometric mean fluorescence intensity (GMFI).