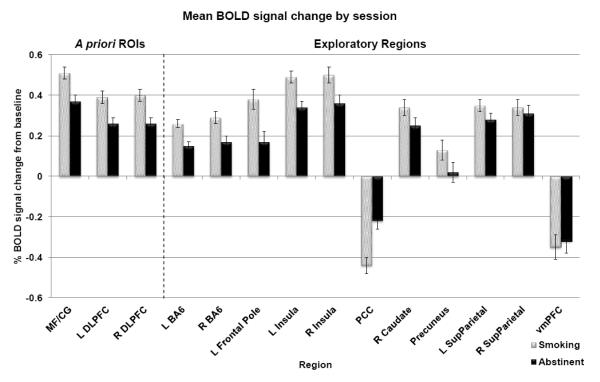
Figure 2. Whole brain results.
Mean percent BOLD signal change from baseline across task levels during abstinent and smoking sessions; bars represent standard error (n=63). In the multiple regression models, percent signal change from baseline was significantly reduced during abstinence in all three a priori ROIs (MF/CG, L DLPFC, and R DLPFC), and in 8 of the 11 additional regions identified by main effect of task (bilateral BA6, left frontal pole, bilateral insula, right caudate, precuneus, and left superior parietal cortex). One region (the PCC) displayed significantly less deactivation below baseline during abstinence. MF/CG = medial frontal/cingulate cortex, DLPFC = dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, BA6 = Brodmann Area 6, PCC = posterior cingulate cortex, SupParietal = superior parietal cortex, vmPFC = ventromedial prefrontal cortex