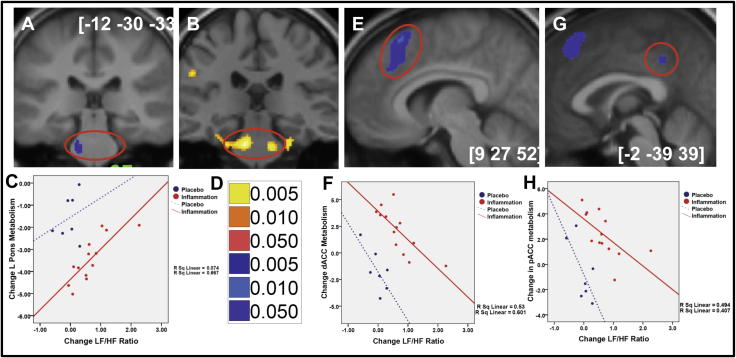
Fig. 4.
Results of whole brain mediation analysis illustrating regions showing a significant mediation of effects of inflammation on blood pressure by change in LF/HF ratio. (A) Left pontine region showing a significant negative mediation by LF/HF ratio change. (B) Location of bilateral pontine correlations with Typhim induced mean arterial pressure change in an earlier independent fMRI study (from Harrison et al. 2009b). (C) Correlation between left pontine FDG uptake and LF/HF change, demonstrating significant reduction in activity following inflammation and interaction between inflammation and change in LF/HF ratio. (D) Statistical threshold for mediation analysis data. (E) dACC region showing a significant negative mediation by LF/HF ratio change. (F) Correlation between dACC FDG uptake and LF/HF change, demonstrating significant increase in activity following inflammation and interaction between inflammation and change in LF/HF ratio. (G) pCC region showing a significant negative mediation by LF/HF ratio change. (H) Correlation between pCC FDG uptake and LF/HF change, demonstrating significant increase in activity following inflammation and interaction between inflammation and change in LF/HF ratio.