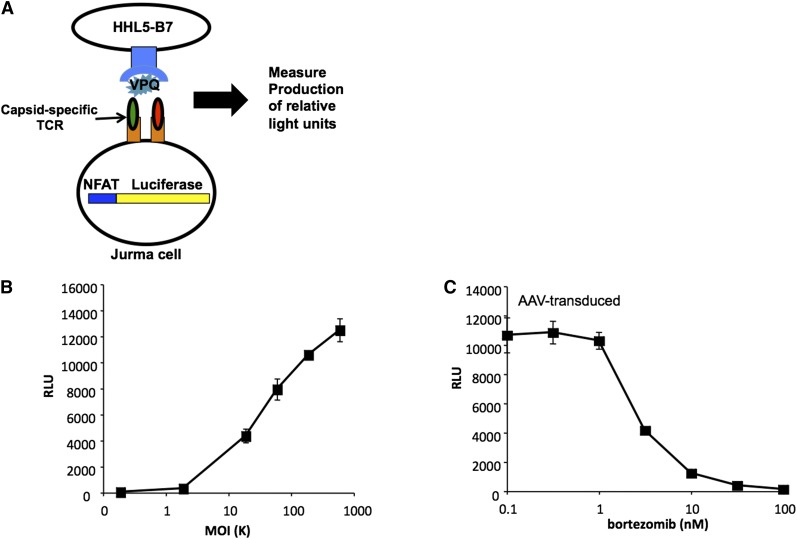
Figure 4.
Capsid antigen presentation is dose-dependent, and can be blocked with a protosomal inhibitor. (A) Generation of a genetically modified T-cell line used as a sensitive detector of peptide-MHC complexes on the cell surface. The T-cell line is stably transfected with a luciferase gene under the control of a promoter containing the NFAT sequence. The cell also carries a TCR cloned from a human subject that recognizes a specific peptide from the AAV capsid complexed with HLA B*0702. Upon engagement of the TCR luciferase is produced. (B) Human hepatocyte cell line HHL5-B7 is transduced with AAV at progressively higher MOIs (x-axis). When the TCR recognizes its cognate peptide-MHC complex, luciferase expression increases (y-axis) in proportion to the number of peptide-MHC complexes engaged. (C) Treatment of cells with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib reduces AAV capsid antigen presentation in a dose-dependent manner. MOI, multiplicity of infection; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; RLU, relative light units. Reprinted from Finn et al.91