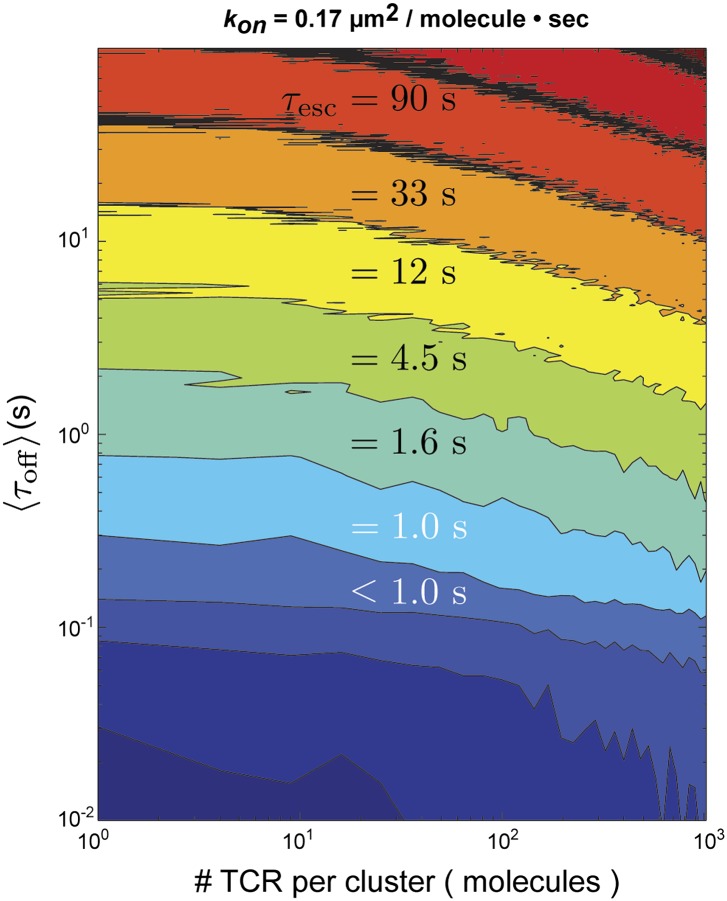
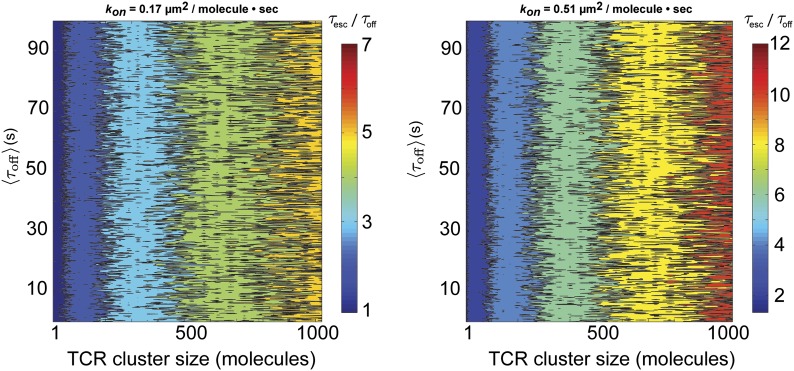
Figure 6. Stochastic reaction-diffusion simulation of time before MCC agonist pMHC escape from TCR clusters, τesc (in color; log scale), as a function of τoff and TCR cluster size.
For small TCR clusters (1–100 TCR molecules) τoff ≈ τesc, indicating no serial rebinding. Only for unrealistically large TCR clusters (1000–10,000 molecules) does become appreciably longer than .