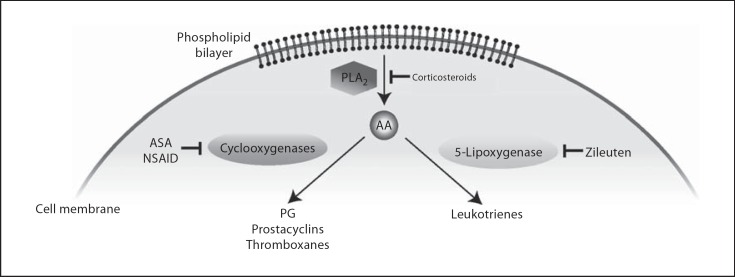
Fig. 1.
Molecular pathways of inflammation via AA formation and downstream induction of cyclooxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase which generate PG and leukotrienes, respectively. While aspirin (ASA) and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAID) inhibit PG, prostacyclin and thromboxane synthesis, corticosteroids act further upstream via inhibition of PLA2, which prevents the release of AA and activation of multiple downstream inflammatory cascades. Zileuton is a targeted 5-lipoxygenase antagonist.