Figure 2. Collagenase-induced intracerebral haemorrhage in a murine model.
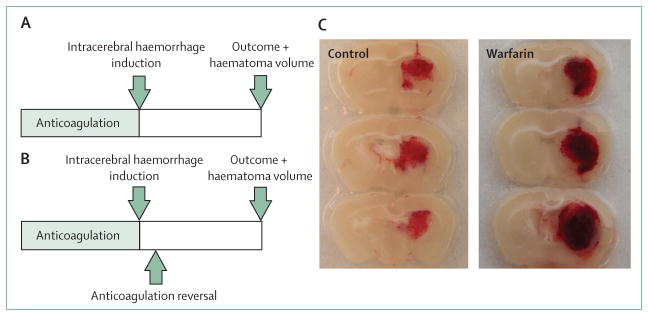
(A) Schematic experimental study protocol. After a defined period of anticoagulation, intracerebral haemorrhage is induced by stereotactic administration of collagenase into the right striatum. After the follow-up period, functional outcome and haematoma volume are measured. (B) Similar study design, but with reversal of anticoagulation after intracerebral haemorrhage induction to assess the effects of haemostatic agents. (C) Representative brain sections obtained 24 h after intracerebral haemorrhage induction in anticoagulation-naive (control) and warfarin-treated (warfarin) animals. Note larger haematoma size, higher clot density, and spots of non-coagulated blood in the warfarin-treated animal.
