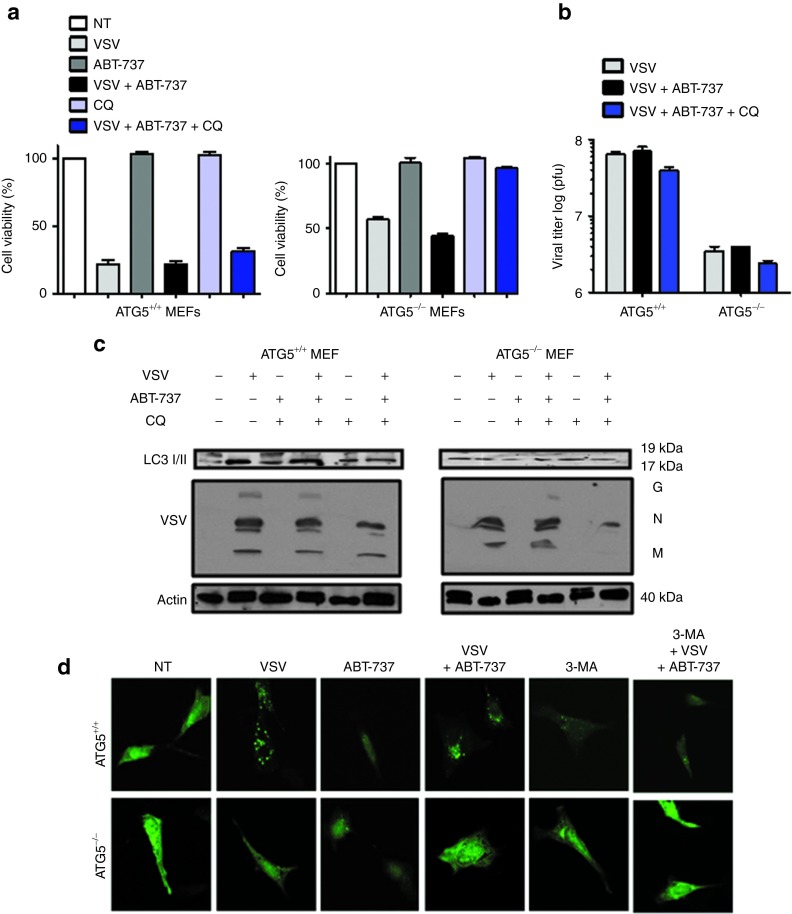
Figure 6.
VSV + ABT-737 combination treatment induces Atg5-mediated cell death. (a) Cell viability analysis was performed on wild-type (WT) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and Atg5 knockout (KO) MEFs treated for 24 hours with VSV (0.1 multiplicity of infection (MOI)) and ABT-737 (5 nmol/l) alone and in combination. Cells were treated or not with CQ (10 μmol/l) for 30 minutes before VSV + ABT-737 therapy. White bars indicate non-treated (NT) cells; light gray bars indicate VSV infection; dark gray bars indicate ABT-737 treatment; black bars indicate VSV + ABT-737 treatment; light blue bars indicate CQ treatment, and dark blue bars indicate VSV + ABT-737 + CQ treatment. (b) WT Atg5 KO MEFs were infected with VSV or ABT-737 alone and in combination followed by inhibition with CQ. Twenty-four hours after infection, the cells and culture supernatants were recovered, and the levels of viral titer were examined by the plaque assay. Viral titers were significantly lower in Atg5 KO MEFs. Light gray bars indicate VSV infection; black bars indicate VSV + ABT-737 treatment, and dark blue bars indicate VSV + ABT-737 + CQ treatment. (c) Western blot measured processing of LC3 and VSV replication in lysates after 24 hours of VSV infection (0.1 MOI). LC3-I (19 kDa) and LC3-II (17 kDa). Viron G, glycoprotein; M, matrix; N, nucleocapsid. (d) WT (top panel) and KO (bottom panel) Atg5 MEFs were transfected with LC3-GFP plasmid, treated with VSV ± ABT-737 and analyzed by immunofluorescence. 3-MA, 3-methyladenine (autophagy inhibitor). Green spots (foci) indicate LC3-GFP localized at autophagosomes. CQ, chloroquine; GFP, green fluorescent protein; pfu, plaque-forming unit; VSV, vesicular stomatitis virus.