Figure 1.
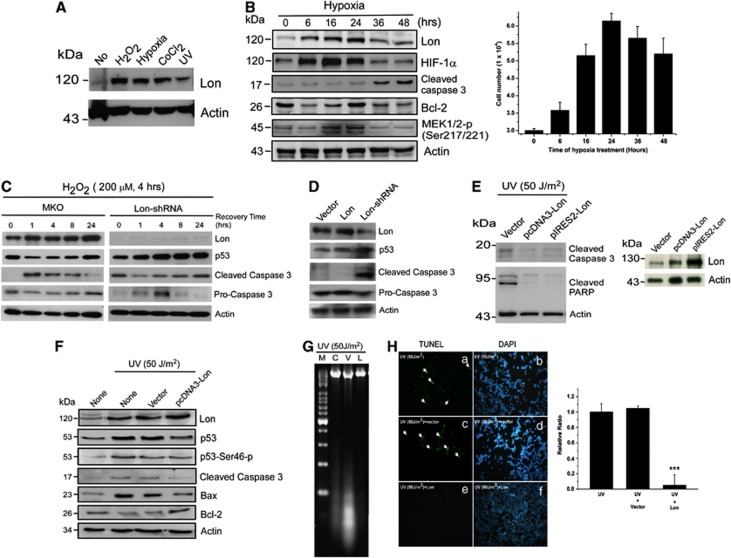
Lon is a stress protein and its level is associated with cell survival. (A) Lon expression is induced with various stresses. Lon protein analysis of 293T cells treated with nothing (No), 200 μM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for 24 h, hypoxia (1% O2) for 24 h, CoCl2 (100 μM) for 24 h, or UV (50 J/m2, recovery for 3 h). The cell extracts were immunoblotted with an antibody to Lon and antibody to actin as a loading control. Result is presented as a representative of three independent experiments. (B) The level of Lon is associated with cell survival under hypoxia 293T cells (3 × 104 cells) were seeded and collected at indicated time point after exposure to hypoxia (1% O2). The protein expression was detected by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. An antibody to Actin was used as a loading control. The viable cells determined by trypan blue dye exclusion assay were shown in right panel. Data are presented as mean±S.D. of at least three independent experiments. (C) The level of Lon is associated with cell survival under oxidative stress 293 cells were retrovirally infected with pMKO vector or pMKO expressing shRNAs for human Lon. Subsequently, these cells were treated with 200 μM H2O2 for 4 h and then incubated for indicated recovery time after the treatment. Immunoblots were probed with indicated antibodies and anti-actin antibody acts as a loading control. The expression of Lon with or without infection of shRNAs was shown. (D) Downregulation of Lon is associated with apoptotic activation FADU cells were retrovirally infected with pMKO vector, Lon-pBABE-puro, or pMKO expressing shRNAs for human Lon. Immunoblots were probed with indicated antibodies and anti-actin antibody acts as a loading control. (E) Overexpression of Lon protects the cells from apoptosis under UV treatment. 293T cells were infected with pcDNA3-Lon, pIRES2-hLon, or vector and treated with UV (50 J/m2, recovery for 3 h). The protein expression was detected by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. An antibody to Actin was used as a loading control (left panel). Exogenous expression of Lon in cells was verified by western blotting with anti-Lon antibody (right panel). The result is a representative of those obtained in at least three individual experiments. (F) Overexpression of Lon protects the cells from UV-induced apoptosis. 293T cells were infected with pcDNA3-Lon or not and treated with UV (50 J/m2). The protein expression was detected by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. An antibody to Actin was used as a loading control. The result is a representative of those obtained in at least three individual experiments. (G) Overexpression of Lon inhibits UV-induced apoptosis shown by DNA fragmentation analysis. DNA fragmentation analysis demonstrated that Lon overexpression prevents UV-induced apoptosis (50 J/m2). M: DNA marker; C: control; V: Vector only; L: Lon overexpression. (H) Overexpression of Lon inhibits UV-induced apoptosis shown by TUNEL assay. 293T cells were transfected with pcDNA3-Lon or not and treated with UV (50 J/m2). TUNEL assay was applied to the transfected cells and the effect of Lon overexpression on UV-induced apoptosis was examined. TUNEL-positive cells (green fluorescence, arrow indicated) were observed in the cells with UV treatment (a) or without Lon overexpression (c), however, no TUNEL-positive cells were detected in the cells with Lon overexpression (e). DAPI was used for nuclear staining. The error bars shown in the right panel represent the S.D. from three different experiments