Figure 2. Immunolocalization of cadherin and Cry11A toxin binding sites in larval gut of 4th instar Ae. aegypti larvae.
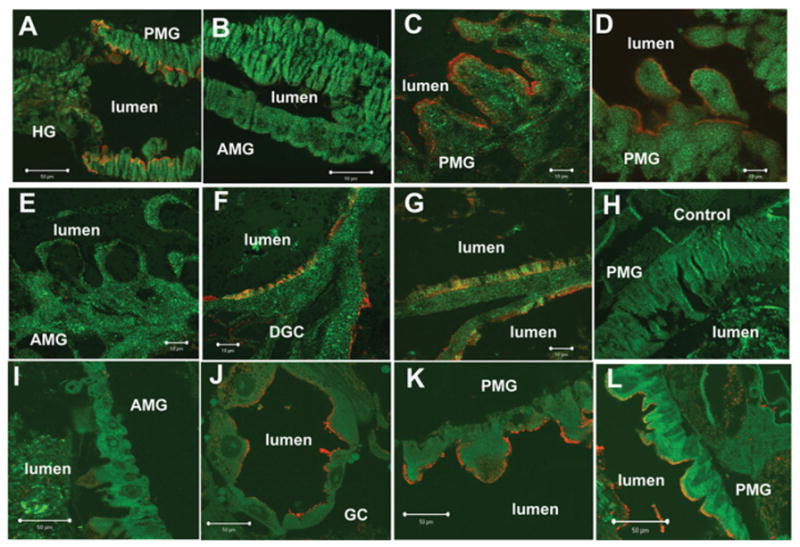
Whole larvae (C–H) and gut sections (A and B) were incubated with affinity purified anti-AaeCad antibody diluted 1:100. Whole larvae sections (I–L) were incubated with Cry11Aa (100 nM) and then with anti-Cry11A antibody diluted 1:1000. Cy3-linked secondary antibody (1:1000, red) was used to determine cadherin localization or Cry11A toxin-binding sites. The cell and tissue structures were visualized by phalloidin (Alexa Fluor® 488, 1:100, green). Red immunofluorescence shows cadherin localization on the apical side of the posterior midgut (A, C and D) but not in the apical membranes of anterior midgut (B and E) and hindgut (A) epithelial cells. Cadherin was also observed on the apical side of distal (F) and proximal (G) gastric caecae. No specific signal was observed in posterior midgut cells when tissues were probed with preimmune serum as a negative control (H). Cry11A toxin bound the apical membrane of epithelial cells in gastric caeca (J) and posterior midgut (K and L). No immunofluorescence was found in the apical membrane of anterior midgut (I). Scale bars, 50 μm (A, B, I–L); 100 μm (C–H). AMG, anterior midgut; DGC, distal gastric caecae; GC, gastric caecae; HG, hindgut; PGC, proximal gastric caecae; PMG, posterior midgut.
