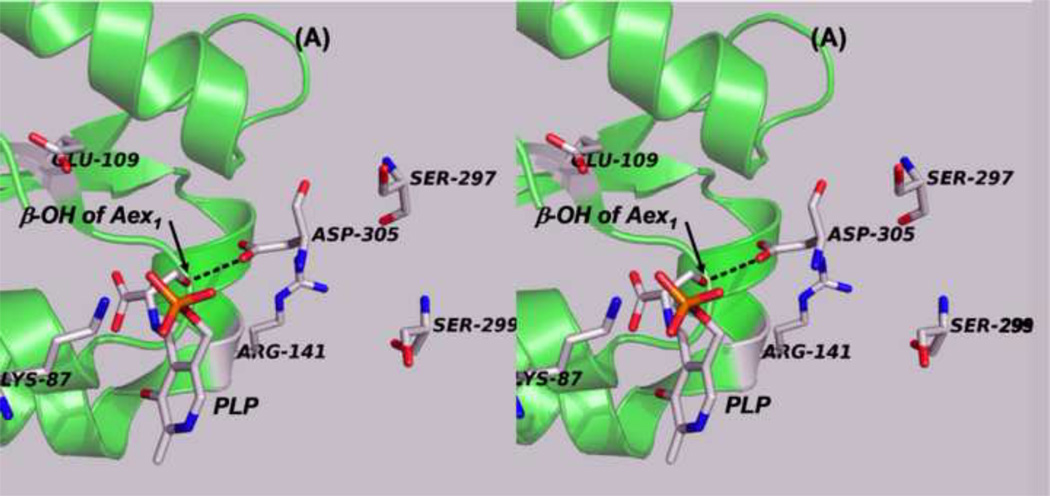
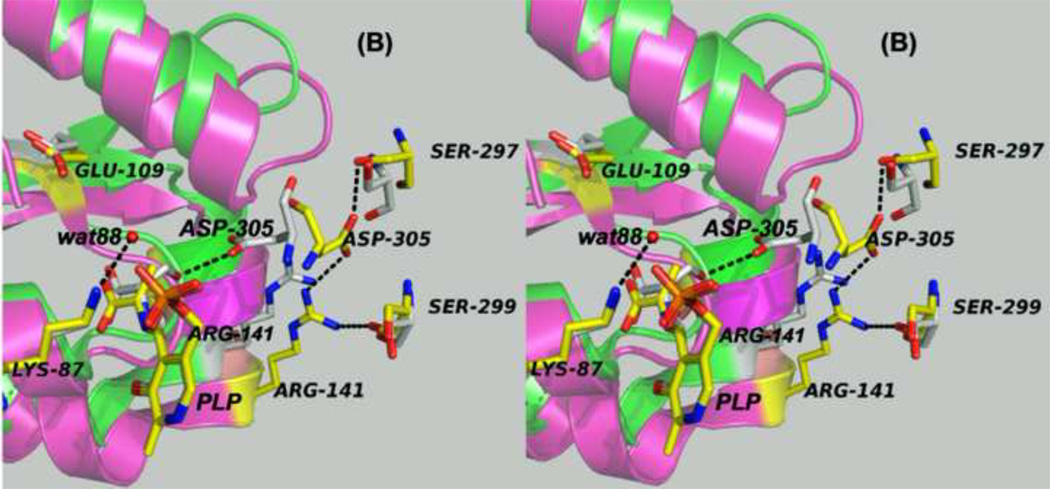
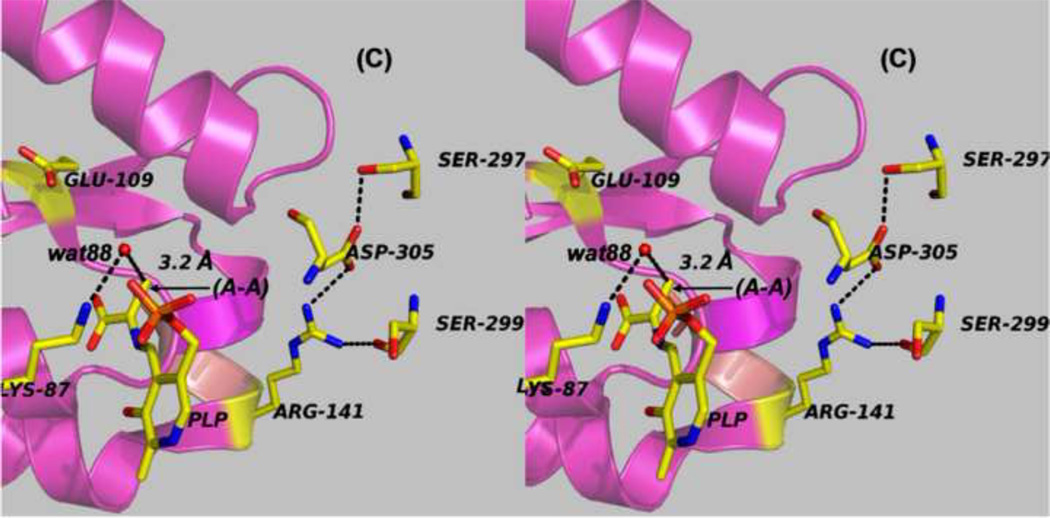
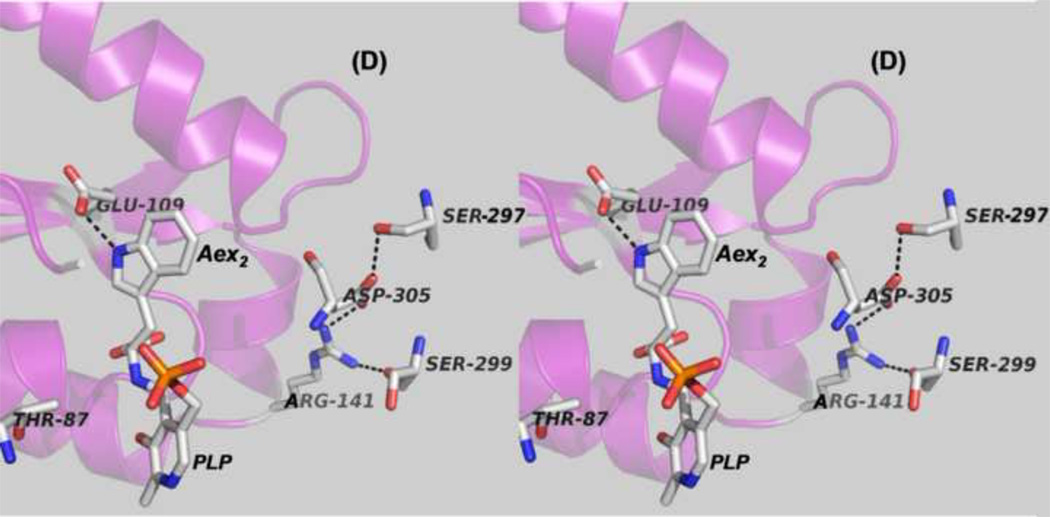
Figure 7.
Panels (A) – (D) present stereo diagrams comparing structural models for the β-active site and the COMM domain (residues β102-β189) of the open and closed β- subunit conformations. (A) Open conformation of the E(Aex1) complex (PDB ID: 2CLL). The β-subunit COMM domain of E(Aex1) is shown as a cartoon ribbon (green), active site residues and the L-Ser moiety (Aex1) bound to PLP are shown as sticks with CPK coloring. In this structure [45] the β-hydroxyl of the Aex1 moiety (black arrow) is hydrogen-bonded (black dashed line) to the carboxylate of βD305. This interaction stabilizes the inactive (open) conformation of E(Aex1) by making removal of the proton chemically more difficult and by preventing bonding interaction(s) with the acid-base catalytic groups at the site, βK87 and βE109. The models in (B) compare the open structure of E(Aex1) from (A) with the closed structure of the α-aminoacrylate intermediate, E(A–A) (PDB ID: 2J9X). The closed structure of the E(A–A) complex is superimposed on the E(Aex1) structure. The COMM domain of E(A–A) is shown as a magenta cartoon ribbon with the active site residues and PLP-bound α-aminoacrylate depicted as stick structures with carbons yellow, and with O, N, and P in CPK colors. Water molecule, wat88, is shown as a red ball, located near the β-carbon of the α-aminoacrylate moiety. Dashed black lines indicate hydrogen bonds. For clarity, the structure of the closed conformation of the E(A–A) complex from (B) is shown in (C). The motion of the COMM domain in the transition from the open to the closed conformation brings βR141 and βD305 together to form a salt bridge along with new hydrogen bonding interactions to βS297 and βS299 [46]. Hydrogen bonds and the distance between the water molecule and the β-carbon of the α-aminoacrylate moiety, (A–A), are indicated by black dashed lines. The βR141-βD305 salt bridge provides a physical barrier which prevents the transfer of ligands between solution and the β- site. This closed conformation also positions βE109 and βK87 for the proton transfers required in the catalytic steps which take place in Stage II of the β- reaction [27, 46, 47, 49].
(D) Stereo structural model showing the closed β-site of the βK87T variant with the L-Trp external aldimine, E(Aex2), bound to the β-site. Notice that the carboxylate of βE109 is hydrogen-bonded to the indole ring N of Aex2 (black dashed line) (PDB ID: 2TYS).